What is E-KYC? A Complete Guide to Electronic Identity Verification
By Dr. Kobkrit Viriyayudhakorn, CEO & Founder, iApp Technology
In today's digital-first world, verifying someone's identity remotely has become essential for businesses across every industry. Whether you're opening a bank account, signing up for a mobile service, or onboarding to a new platform, E-KYC (Electronic Know Your Customer) makes it possible to verify your identity in seconds rather than days.
This comprehensive guide will explain what E-KYC is, why it matters, how it works technically, and provide hands-on tutorials to implement E-KYC in your applications using iApp Technology's APIs.
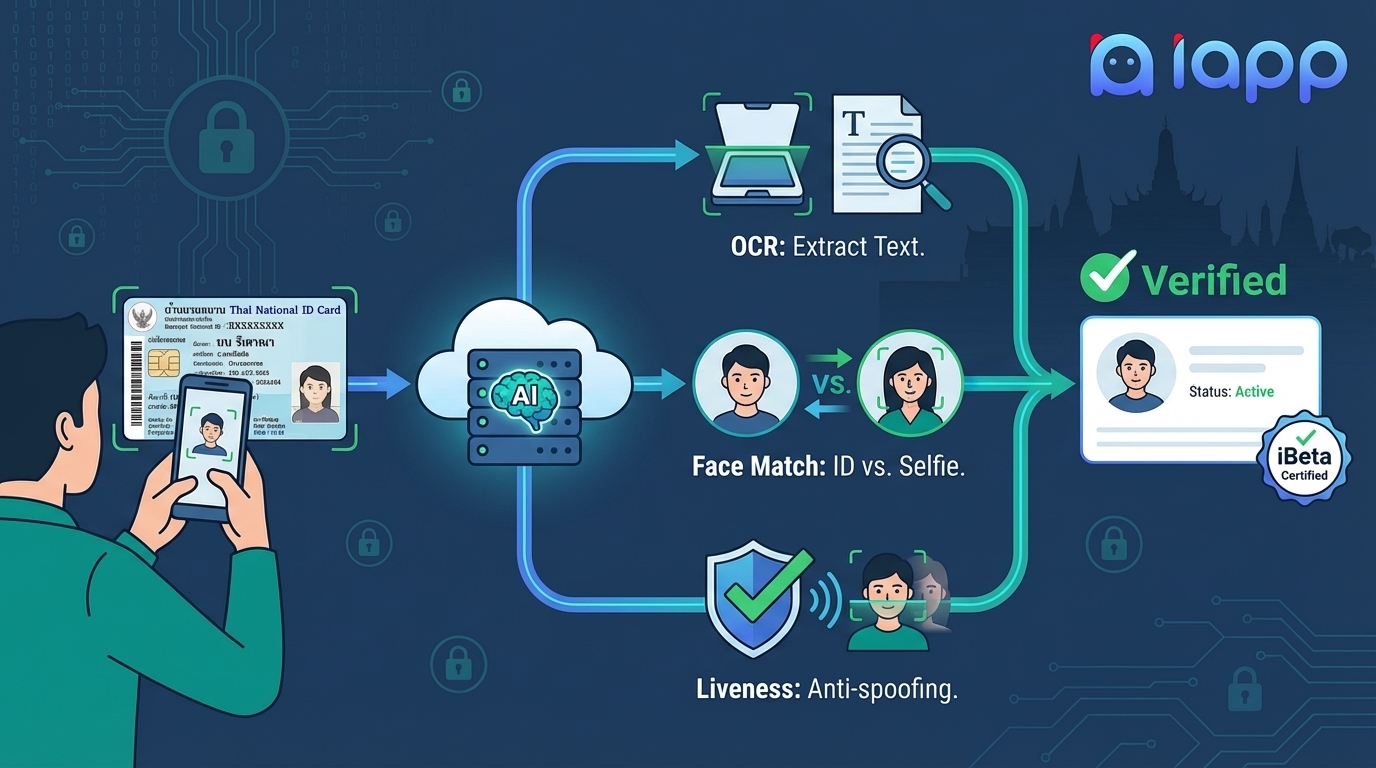
Table of Contents
- What is E-KYC?
- Why is E-KYC Important?
- Components of E-KYC
- Document OCR Technologies
- Face Verification
- Liveness Detection: Active vs Passive
- Understanding Face Spoofing
- iBeta Certification
- Hands-On Tutorial
- Best Practices
What is E-KYC?
E-KYC stands for Electronic Know Your Customer. It is the digital process of verifying a person's identity remotely using electronic means, eliminating the need for physical document submission or in-person verification.
Traditional KYC vs E-KYC
| Aspect | Traditional KYC | E-KYC |
|---|---|---|
| Location | In-person at branch/office | Anywhere with internet |
| Time | Days to weeks | Minutes to seconds |
| Documents | Physical copies required | Digital photos/scans |
| Verification | Manual review by staff | AI-powered automation |
| Cost | High (staff, storage, logistics) | Low (automated) |
| User Experience | Inconvenient | Seamless |
| Scalability | Limited | Unlimited |
The E-KYC Process Flow
Why is E-KYC Important?
1. Regulatory Compliance
Financial institutions, telecommunications companies, and many other industries are legally required to verify customer identities. E-KYC helps meet regulations such as:
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws
- Counter-Terrorism Financing (CTF) requirements
- PDPA (Thailand's Personal Data Protection Act)
- GDPR (EU's General Data Protection Regulation)
2. Fraud Prevention
E-KYC with liveness detection prevents:
- Identity theft - Using someone else's documents
- Synthetic identity fraud - Creating fake identities
- Account takeover - Unauthorized access to accounts
- Money laundering - Using fake identities to move illegal funds
3. Business Benefits
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Faster Onboarding | Convert customers in minutes, not days |
| Lower Costs | Reduce manual verification costs by 70-90% |
| Better Experience | Customers can verify from anywhere, anytime |
| Higher Conversion | Less drop-off during registration |
| Scalability | Handle millions of verifications automatically |
4. Industry Applications
| Industry | E-KYC Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Banking | Account opening, loan applications, credit cards |
| Fintech | Digital wallets, P2P lending, investment apps |
| Insurance | Policy applications, claims processing |
| Telecom | SIM card registration, mobile contracts |
| Healthcare | Patient registration, telemedicine |
| Government | Digital ID, e-voting, public services |
| Real Estate | Rental agreements, property purchases |
| E-commerce | Seller verification, high-value purchases |
Components of E-KYC
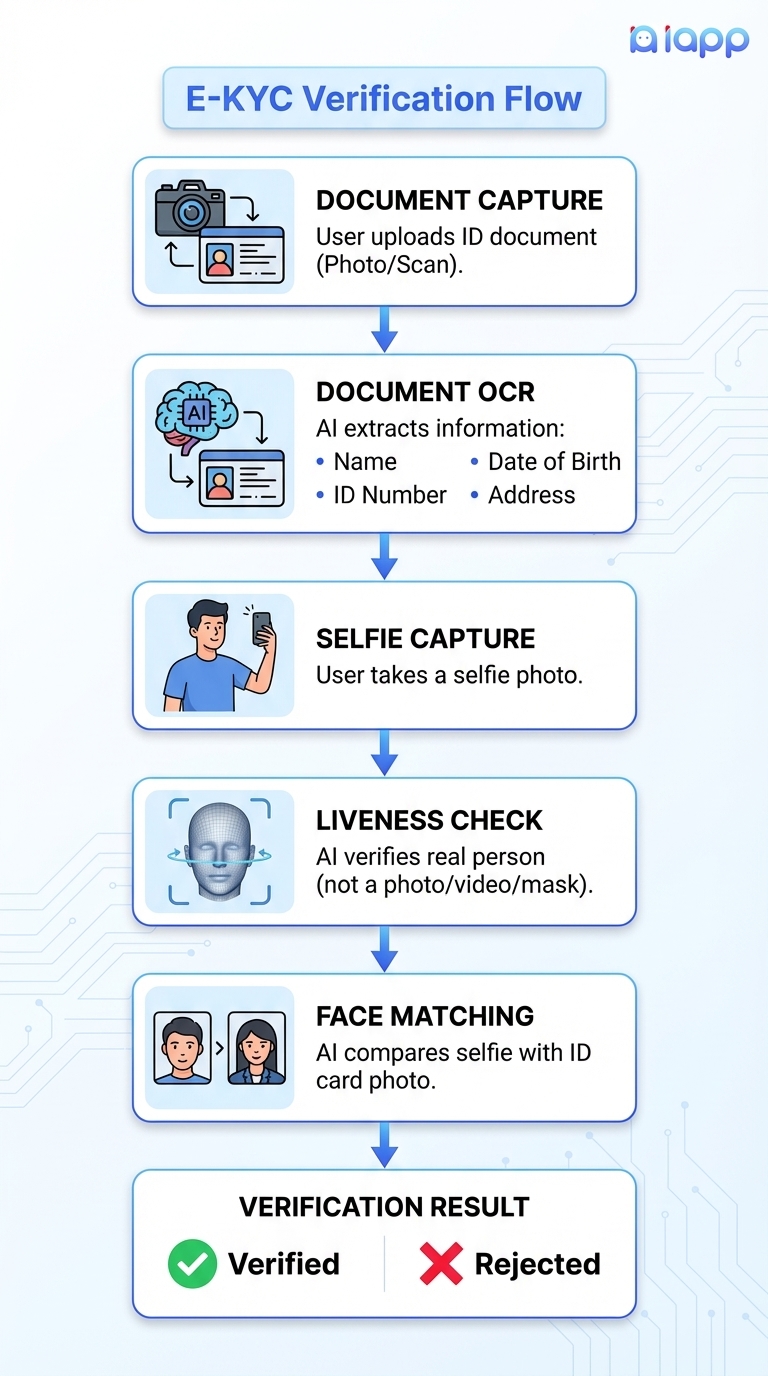
A complete E-KYC system consists of four main components:
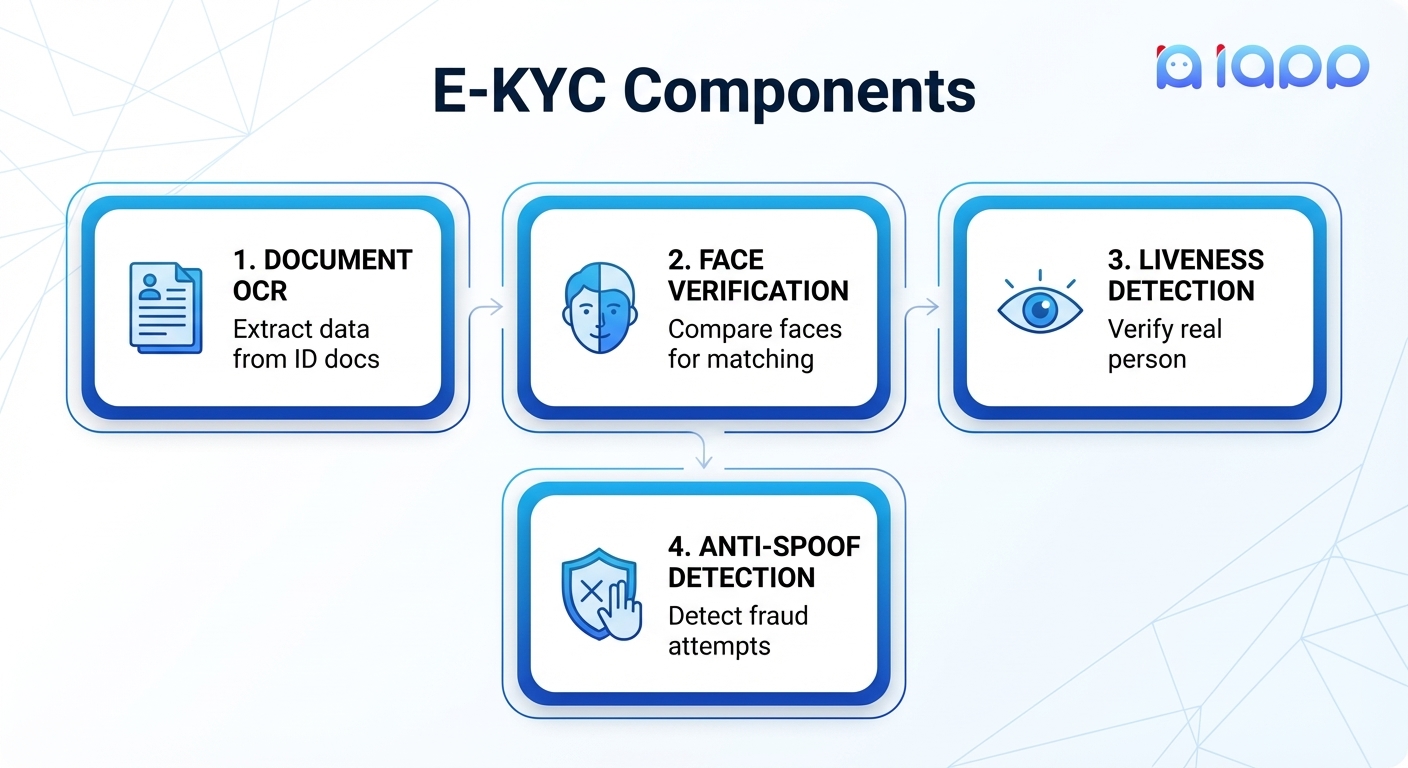
Document OCR Technologies
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) is the technology that extracts text and data from document images. In E-KYC, specialized OCR is used for identity documents.
Supported Document Types
1. Thai National ID Card OCR
The Thai National ID Card is the most commonly used document for E-KYC in Thailand. iApp's OCR API extracts:
Front Side:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
id_number | 13-digit National ID number |
th_name / en_name | Full name in Thai and English |
th_dob / en_dob | Date of birth |
address | Full registered address |
province, district, sub_district | Location breakdown |
th_issue / th_expire | Issue and expiry dates |
religion | Religion (if present) |
face | Extracted face photo (Base64) |
Back Side:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
back_number | Laser code for verification |
API Endpoint: POST /v3/store/ekyc/thai-national-id-card/front
Accuracy: 98.13% at character level
2. Thai Driver License OCR
Extract information from Thai driver licenses for identity verification and driving-related services.
Extracted Fields:
- License number
- Name (Thai/English)
- Date of birth
- License type and class
- Issue and expiry dates
- Address
API Endpoint: POST /v3/store/ekyc/thai-driver-license
3. Thai Bank Book OCR
Extract account information from Thai bank passbook images for financial verification.
Extracted Fields:
- Account number
- Account holder name
- Bank name and branch
- Account type
API Endpoint: POST /v3/store/ekyc/book-bank
4. Passport OCR
Extract information from international passports, including MRZ (Machine Readable Zone) data.
Extracted Fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
passport_number | Passport document number |
surname / given_name | Full name |
nationality | Country of citizenship |
date_of_birth | Birth date |
sex | Gender |
expiry_date | Passport expiration |
mrz_line1 / mrz_line2 | Machine readable zone data |
face | Extracted face photo |
API Endpoint: POST /v3/store/ekyc/passport
Face Verification
Face Verification compares two face images to determine if they belong to the same person. This is crucial for confirming that the person presenting the ID document is actually the document's owner.
How Face Verification Works
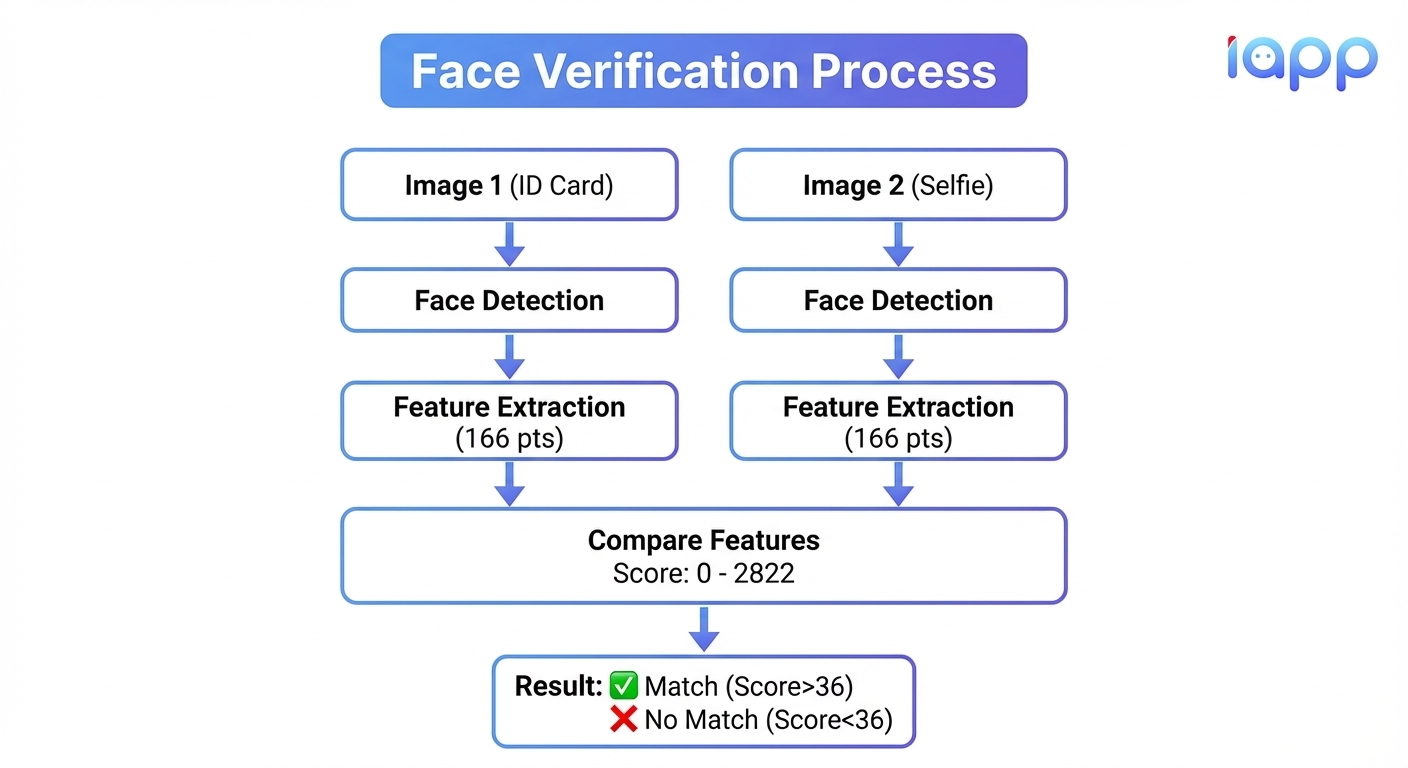
Understanding Similarity Scores
The similarity score ranges from 0 to 2822, calculated from face template matching of 166 facial points.
| Threshold | Precision | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| 36 | 99.50% | Standard verification |
| 48 | 99.95% | High-security applications |
API Endpoint: POST /v3/store/ekyc/face-verification
Example Response:
{
"matched": true,
"score": 38.0,
"threshold": 37,
"duration": 2.13,
"message": "successfully performed"
}
Liveness Detection: Active vs Passive
Liveness Detection ensures that the face being verified belongs to a real, live person present at the time of verification—not a photo, video, or mask.
Active Liveness vs Passive Liveness
| Aspect | Active Liveness | Passive Liveness |
|---|---|---|
| User Action | Requires actions (blink, turn head, smile) | Single photo, no actions needed |
| User Experience | More friction, takes longer | Seamless, instant |
| Security Level | Very high | High (iBeta Level 1) |
| Spoofing Detection | Real-time challenge-response | AI analysis of single image |
| Implementation | More complex (video/SDK) | Simple (single API call) |
| Best For | High-security transactions | Mass onboarding, balance of UX/security |
Active Liveness Detection
Active liveness requires the user to perform specific actions:
- Blink detection - User must blink naturally
- Head movement - Turn head left/right/up/down
- Facial expressions - Smile, open mouth
- Random challenges - Unpredictable sequence of actions
Pros:
- Very difficult to spoof
- Proves real-time presence
- Higher security assurance
Cons:
- Poor user experience
- Higher drop-off rates
- Requires SDK/video capture
- Accessibility issues (disabilities)
Passive Liveness Detection
Passive liveness analyzes a single photo using AI to detect spoofing attempts without requiring user actions.
What it detects:
- Printed photos
- Screen displays (phone/computer)
- Realistic face masks
- Video replays
- Paper cutouts
How it works:
- Analyzes texture patterns
- Detects screen moiré patterns
- Identifies paper/printing artifacts
- Checks depth and 3D characteristics
- Analyzes lighting consistency
API Endpoint: POST /v3/store/ekyc/face-passive-liveness
Example Response:
{
"predict": "REAL",
"score": 0.0001234,
"darkness": 0.42,
"data": {
"SPOOF": 0.0001234,
"REAL": 0.9998766
},
"message": "SUCCESS"
}
When to Use Which?
| Scenario | Recommended Approach |
|---|---|
| Opening bank account | Active + Passive |
| Mobile app registration | Passive only |
| High-value transactions | Active |
| Quick verification | Passive only |
| Government services | Active + Passive |
| E-commerce seller verification | Passive only |
Understanding Face Spoofing
Face Spoofing (also called Presentation Attack) is an attempt to fool a face recognition system by presenting a fake face instead of the genuine person.
Types of Face Spoofing Attacks
1. Print Attacks
- Description: Using a printed photo of the victim
- Detection: Paper texture, flat surface, lack of depth
2. Screen/Replay Attacks
- Description: Displaying victim's photo/video on a screen
- Detection: Screen moiré patterns, pixel artifacts, refresh rate
3. 3D Mask Attacks
- Description: Wearing a realistic 3D mask of the victim
- Detection: Texture analysis, skin detection, eye movement
4. Deepfake Attacks
- Description: AI-generated fake video of the victim
- Detection: Temporal inconsistencies, unnatural movements

Why Anti-Spoofing Matters
Without anti-spoofing protection:
- Criminals can open accounts using stolen ID photos
- Account takeover becomes trivial
- Financial fraud increases significantly
- Trust in digital services erodes
iBeta Certification
iBeta is an independent testing laboratory that certifies biometric systems for Presentation Attack Detection (PAD). iBeta certification is the gold standard for proving that a liveness detection system is secure.
iBeta PAD Levels
| Level | Description | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Basic PAD | Must detect common attacks (print, screen) |
| Level 2 | Advanced PAD | Must detect sophisticated attacks (3D masks, advanced spoofs) |
What iBeta Tests
- Print Attacks - Various paper types, sizes, and qualities
- Screen Attacks - Different devices (phones, tablets, monitors)
- Artifact Species - Multiple presentation instruments
- Environmental Conditions - Various lighting scenarios
iApp Technology's iBeta Certification
iApp Technology's Face Passive Liveness Detection has achieved iBeta PAD Level 1 certification with:
- 99.43% accuracy across 7,680 tests
- Detection of printed photos
- Detection of screen displays
- Detection of realistic masks
- Detection of video replays
Hands-On Tutorial
Let's build a complete E-KYC verification flow using iApp Technology's APIs.
Prerequisites
- API key from iApp Technology
- Python 3.x or Node.js installed
- Test images (ID card, selfie)
Step 1: Thai ID Card OCR
Extract information from a Thai National ID card.
Python
import requests
import json
API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY"
def extract_id_card(image_path):
"""Extract information from Thai ID card front side"""
url = "https://api.iapp.co.th/v3/store/ekyc/thai-national-id-card/front"
with open(image_path, 'rb') as image_file:
files = {'file': image_file}
headers = {'apikey': API_KEY}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, files=files)
return response.json()
# Example usage
result = extract_id_card("thai_id_card.jpg")
print("=== Thai ID Card OCR Results ===")
print(f"ID Number: {result.get('id_number')}")
print(f"Name (TH): {result.get('th_name')}")
print(f"Name (EN): {result.get('en_name')}")
print(f"Date of Birth: {result.get('en_dob')}")
print(f"Address: {result.get('address')}")
print(f"Detection Score: {result.get('detection_score'):.2%}")
JavaScript (Node.js)
const axios = require('axios');
const FormData = require('form-data');
const fs = require('fs');
const API_KEY = 'YOUR_API_KEY';
async function extractIdCard(imagePath) {
const url = 'https://api.iapp.co.th/v3/store/ekyc/thai-national-id-card/front';
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('file', fs.createReadStream(imagePath));
const response = await axios.post(url, formData, {
headers: {
'apikey': API_KEY,
...formData.getHeaders()
}
});
return response.data;
}
// Example usage
extractIdCard('thai_id_card.jpg').then(result => {
console.log('=== Thai ID Card OCR Results ===');
console.log(`ID Number: ${result.id_number}`);
console.log(`Name (TH): ${result.th_name}`);
console.log(`Name (EN): ${result.en_name}`);
console.log(`Date of Birth: ${result.en_dob}`);
});
Step 2: Face Liveness Check
Verify the selfie is from a real person.
Python
def check_liveness(selfie_path):
"""Check if the face is from a real person (not spoofed)"""
url = "https://api.iapp.co.th/v3/store/ekyc/face-passive-liveness"
with open(selfie_path, 'rb') as image_file:
files = {'file': image_file}
headers = {'apikey': API_KEY}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, files=files)
return response.json()
# Example usage
liveness_result = check_liveness("selfie.jpg")
print("\n=== Liveness Check Results ===")
print(f"Prediction: {liveness_result.get('predict')}")
print(f"Is Real: {liveness_result.get('predict') == 'REAL'}")
print(f"Spoof Score: {liveness_result.get('score'):.6f}")
if liveness_result.get('predict') == 'SPOOF':
print("⚠️ WARNING: Possible spoofing attempt detected!")
else:
print("✅ Real person detected")
Step 3: Face Verification
Compare the ID card photo with the selfie.
Python
def verify_faces(id_card_path, selfie_path, threshold=36):
"""Compare two face images to verify same person"""
url = "https://api.iapp.co.th/v3/store/ekyc/face-verification"
files = {
'file1': open(id_card_path, 'rb'),
'file2': open(selfie_path, 'rb')
}
headers = {'apikey': API_KEY}
data = {'threshold': threshold}
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, files=files, data=data)
# Close files
files['file1'].close()
files['file2'].close()
return response.json()
# Example usage
verification_result = verify_faces("id_card_face.jpg", "selfie.jpg")
print("\n=== Face Verification Results ===")
print(f"Matched: {verification_result.get('matched')}")
print(f"Score: {verification_result.get('score')}")
print(f"Threshold: {verification_result.get('threshold')}")
if verification_result.get('matched'):
print("✅ Identity verified - Same person")
else:
print("❌ Verification failed - Different person or low quality")
Step 4: Complete E-KYC Flow
Combine all steps into a complete verification flow.
Python
def complete_ekyc_verification(id_card_path, selfie_path):
"""
Complete E-KYC verification flow:
1. Extract ID card information
2. Check selfie liveness
3. Verify face match
"""
results = {
'success': False,
'steps': {},
'errors': []
}
# Step 1: Extract ID card information
print("Step 1: Extracting ID card information...")
id_result = extract_id_card(id_card_path)
results['steps']['id_card_ocr'] = id_result
if not id_result.get('id_number'):
results['errors'].append("Failed to extract ID card information")
return results
print(f" ✅ ID Number: {id_result.get('id_number')}")
print(f" ✅ Name: {id_result.get('en_name')}")
# Step 2: Check liveness
print("\nStep 2: Checking liveness...")
liveness_result = check_liveness(selfie_path)
results['steps']['liveness'] = liveness_result
if liveness_result.get('predict') == 'SPOOF':
results['errors'].append("Liveness check failed - Possible spoofing detected")
return results
print(f" ✅ Real person confirmed")
# Step 3: Verify face match
print("\nStep 3: Verifying face match...")
verification_result = verify_faces(id_card_path, selfie_path)
results['steps']['face_verification'] = verification_result
if not verification_result.get('matched'):
results['errors'].append("Face verification failed - Faces do not match")
return results
print(f" ✅ Face matched (Score: {verification_result.get('score')})")
# All checks passed
results['success'] = True
results['verified_identity'] = {
'id_number': id_result.get('id_number'),
'name_th': id_result.get('th_name'),
'name_en': id_result.get('en_name'),
'date_of_birth': id_result.get('en_dob'),
'address': id_result.get('address')
}
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("🎉 E-KYC VERIFICATION SUCCESSFUL!")
print("="*50)
return results
# Run complete verification
result = complete_ekyc_verification("thai_id_card.jpg", "selfie.jpg")
if result['success']:
print(f"\nVerified Identity:")
print(json.dumps(result['verified_identity'], indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
else:
print(f"\nVerification Failed:")
for error in result['errors']:
print(f" ❌ {error}")
Best Practices
1. Image Quality Requirements
| Factor | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Resolution | Minimum 600x400 pixels |
| Format | JPEG, PNG, HEIC, HEIF |
| Size | Under 10MB for OCR, 2MB for face |
| Lighting | Even, natural lighting preferred |
| Focus | Sharp, not blurry |
| Angle | Face frontal, document flat |
2. Security Best Practices
# ✅ GOOD: Use environment variables
import os
API_KEY = os.environ.get('IAPP_API_KEY')
# ❌ BAD: Hardcoded API key
API_KEY = "sk-1234567890"
# ✅ GOOD: Always check liveness before face verification
if liveness_result['predict'] == 'REAL':
verification_result = verify_faces(...)
# ❌ BAD: Skip liveness check
verification_result = verify_faces(...) # Vulnerable to spoofing!
# ✅ GOOD: Use appropriate thresholds
verify_faces(..., threshold=48) # High security
# ❌ BAD: Use low thresholds
verify_faces(..., threshold=20) # Too permissive!
3. Error Handling
def safe_ekyc_call(func, *args, **kwargs):
"""Wrapper for safe E-KYC API calls"""
try:
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
# Check for API errors
if 'error_message' in result and result['error_message']:
raise Exception(f"API Error: {result['error_message']}")
return result
except requests.exceptions.Timeout:
raise Exception("Request timeout - please try again")
except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError:
raise Exception("Connection error - check your internet")
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"E-KYC verification failed: {str(e)}")
4. Compliance Considerations
- Data Retention: Don't store biometric data longer than necessary
- User Consent: Always obtain explicit consent before E-KYC
- Data Encryption: Encrypt all biometric data in transit and at rest
- Audit Logs: Maintain logs for compliance auditing
- Right to Erasure: Enable users to request data deletion
Summary
E-KYC is a powerful technology that enables businesses to verify customer identities digitally. A complete E-KYC solution includes:
- Document OCR - Extract information from ID documents
- Face Verification - Compare faces to confirm identity
- Liveness Detection - Ensure real person is present
- Anti-Spoofing - Prevent fraud attempts
Key takeaways:
- Choose Passive Liveness for better UX, Active Liveness for higher security
- Always implement anti-spoofing to prevent fraud
- Look for iBeta certification when choosing providers
- Follow security best practices and compliance requirements
Resources
- Thai ID Card OCR Documentation
- Face Verification Documentation
- Face Liveness Detection Documentation
- API Key Management
- Pricing Calculator
- iBeta Certificate
About the Author
Dr. Kobkrit Viriyayudhakorn is the CEO and Founder of iApp Technology, Thailand's leading AI company specializing in E-KYC, OCR, and biometric verification. With iBeta PAD Level 1 and Level 2 certifications, iApp Technology serves over 100 enterprise customers including banks, insurance companies, and telecommunications providers.
References
- iBeta Quality Assurance, "Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) Testing", 2024
- NIST, "Biometric Quality Standards", 2024
- Bank of Thailand, "Digital Banking Guidelines", 2024
- PDPC Thailand, "Personal Data Protection Act Guidelines", 2024
- ISO/IEC 30107-3, "Biometric Presentation Attack Detection", 2023