What is Big Data? A Complete Guide for Beginners
Every second, the world generates an unimaginable amount of data. Every Google search, every social media post, every online purchase, every sensor reading — it all adds up. In fact, we create approximately 2.5 quintillion bytes of data every single day. This massive flood of information is what we call Big Data, and learning how to harness it has become one of the most valuable skills in the modern business world.
What is Big Data?
Big Data refers to extremely large and complex datasets that are too big for traditional data processing tools to handle efficiently. But it's not just about size — Big Data is defined by its unique characteristics that make it challenging and valuable.
At its core, Big Data is:
- Too large for conventional databases
- Too fast — generated in real-time streams
- Too varied — coming in many different formats
- Too complex for simple analysis tools
The goal of Big Data isn't just to collect massive amounts of information — it's to analyze this data to discover patterns, trends, and insights that can drive better decisions.
Simple Example
Traditional Data:
- A small shop tracks daily sales in a spreadsheet
- 100 transactions per day, easily managed in Excel
- Simple calculations like monthly totals and averages
Big Data:
- An e-commerce platform processes millions of transactions daily
- Tracks user behavior: clicks, searches, time on page, cart abandonment
- Combines with social media sentiment, weather data, economic indicators
- Uses AI to predict trends, personalize recommendations, optimize pricing
The 5 V's of Big Data
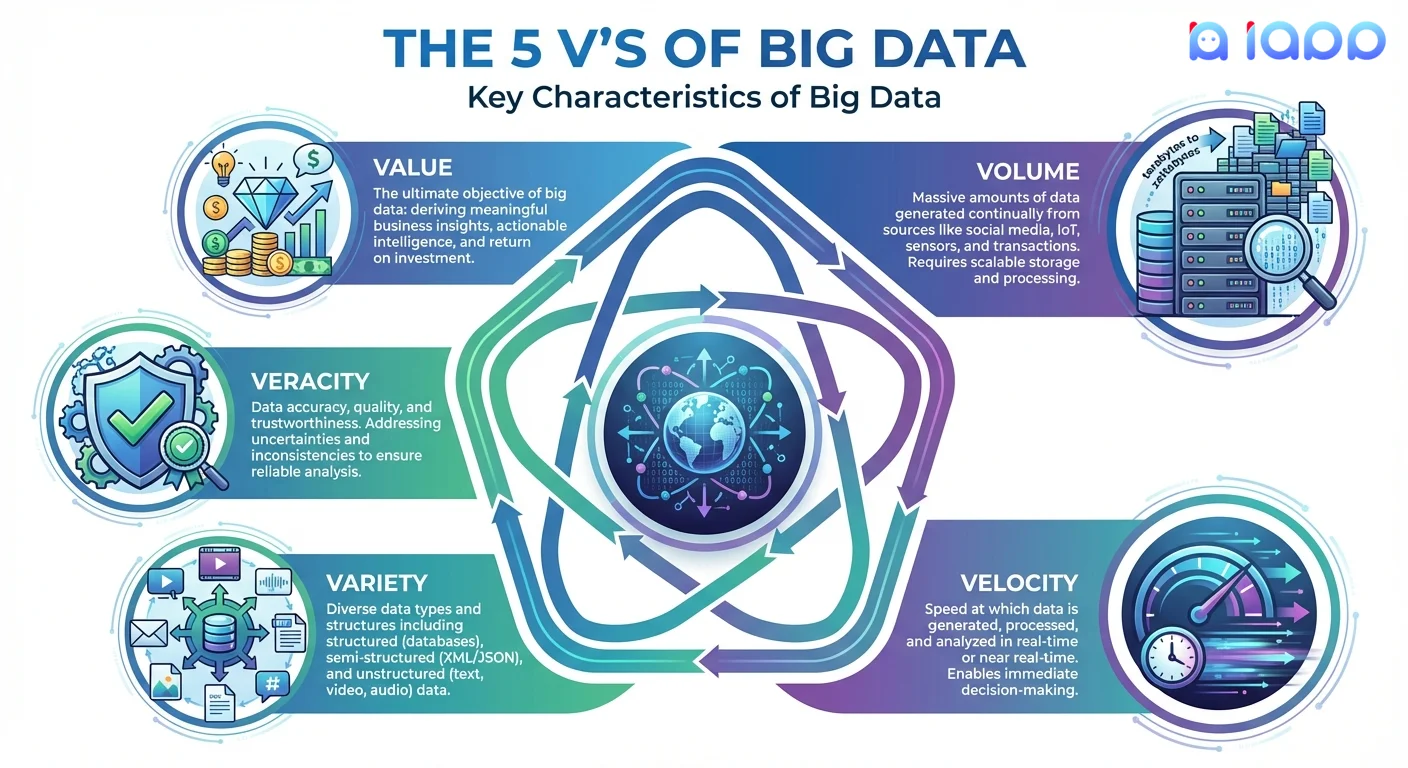
Big Data is commonly defined by five key characteristics:
1. Volume
The sheer amount of data being generated.
- Facebook users upload 350 million photos daily
- YouTube receives 500 hours of video every minute
- IoT sensors generate billions of data points continuously
Challenge: Storing and managing petabytes or exabytes of data
2. Velocity
The speed at which data is created and needs to be processed.
- Stock market data changes millisecond by millisecond
- Social media posts go viral in minutes
- Sensor data streams in real-time continuously
Challenge: Processing data fast enough to act on it in time
3. Variety
The different types and formats of data.
- Structured: Databases, spreadsheets, transaction records
- Semi-structured: JSON, XML, emails, logs
- Unstructured: Images, videos, audio, social media posts, documents
Challenge: Integrating and analyzing diverse data types together
4. Veracity
The accuracy and trustworthiness of data.
- Is the data correct and reliable?
- How do we handle missing or incomplete data?
- Can we trust the source?
Challenge: Ensuring data quality before making decisions
5. Value
The business worth that can be extracted from data.
- Raw data is useless without analysis
- The goal is actionable insights
- ROI must justify the cost of Big Data infrastructure
Challenge: Finding meaningful patterns among the noise
Types of Big Data
1. Structured Data
Organized data that fits neatly into tables with rows and columns.
Examples:
- Database records
- Spreadsheets
- Transaction logs
- Sensor readings with defined formats
Characteristics: Easy to search, analyze, and process Storage: Traditional relational databases (SQL)
2. Semi-Structured Data
Data with some organizational properties but not rigid structure.
Examples:
- JSON and XML files
- Email messages
- Web server logs
- NoSQL database documents
Characteristics: Flexible schema, self-describing Storage: NoSQL databases, document stores
3. Unstructured Data
Data without predefined format or organization.
Examples:
- Text documents and PDFs
- Images and photos
- Audio and video files
- Social media posts
Characteristics: Hardest to analyze, requires AI/ML Storage: Data lakes, object storage
Fun fact: Over 80% of enterprise data is unstructured, and this is where AI shines!
Key Big Data Terms Explained (Jargon Buster)
1. Data Lake
What it is: A centralized repository that stores all types of data in their raw, native format.
Simple analogy: Like a real lake where different streams (data sources) flow in. You can fish anywhere for any type of fish (data).
Key features:
- Stores structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data
- Schema-on-read (structure applied when data is accessed)
- Cost-effective for massive storage
- Ideal for AI/ML and exploration
2. Data Warehouse
What it is: A structured, organized repository optimized for analysis and reporting.
Simple analogy: Like a well-organized warehouse where everything has a specific place and label. Easy to find what you need.
Key features:
- Stores structured, processed data
- Schema-on-write (structure defined before storage)
- Optimized for fast queries
- Ideal for business intelligence and dashboards
3. ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
What it is: The process of moving data from sources to a destination, transforming it along the way.
Simple analogy: Like sorting, cleaning, and organizing groceries from shopping bags into your kitchen cabinets.
Steps:
- Extract: Pull data from various sources
- Transform: Clean, validate, convert formats
- Load: Store in the destination system
4. Data Pipeline
What it is: An automated series of processes that move and transform data from source to destination.
Simple analogy: Like a factory assembly line where raw materials enter one end and finished products come out the other.
Components:
- Data ingestion (collection)
- Data processing (transformation)
- Data storage (warehousing)
- Data analysis (insights)
5. Real-Time Analytics
What it is: Processing and analyzing data immediately as it's generated.
Simple analogy: Like a live sports scoreboard that updates instantly with every play.
Use cases:
- Fraud detection
- Stock trading
- IoT monitoring
- Live dashboards
Why Big Data Matters
1. Better Decision Making
Data-driven decisions outperform gut feelings. Companies using Big Data analytics are:
- 5x more likely to make faster decisions
- 3x more likely to execute decisions as intended
2. Understanding Customers
Big Data reveals:
- What customers actually want (not what they say)
- Behavioral patterns and preferences
- Churn prediction and prevention
- Personalization opportunities
3. Operational Efficiency
Optimize operations by:
- Predictive maintenance (fix before it breaks)
- Supply chain optimization
- Resource allocation
- Process automation
4. New Revenue Streams
Create value through:
- Data products and services
- Personalized offerings
- Dynamic pricing
- New market insights
5. Competitive Advantage
Companies leveraging Big Data effectively can:
- Respond faster to market changes
- Identify trends before competitors
- Innovate based on insights
- Reduce costs while improving quality
What Problems Does Big Data Solve?
| Problem | Traditional Approach | Big Data Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Customer insights | Surveys & focus groups | Behavioral analytics at scale |
| Fraud detection | Manual review, rules | Real-time AI pattern detection |
| Inventory management | Historical averages | Predictive demand forecasting |
| Marketing effectiveness | Campaign metrics | Attribution modeling, personalization |
| Quality control | Sample testing | 100% automated inspection |
| Risk assessment | Manual analysis | ML risk scoring models |
How Big Data Works
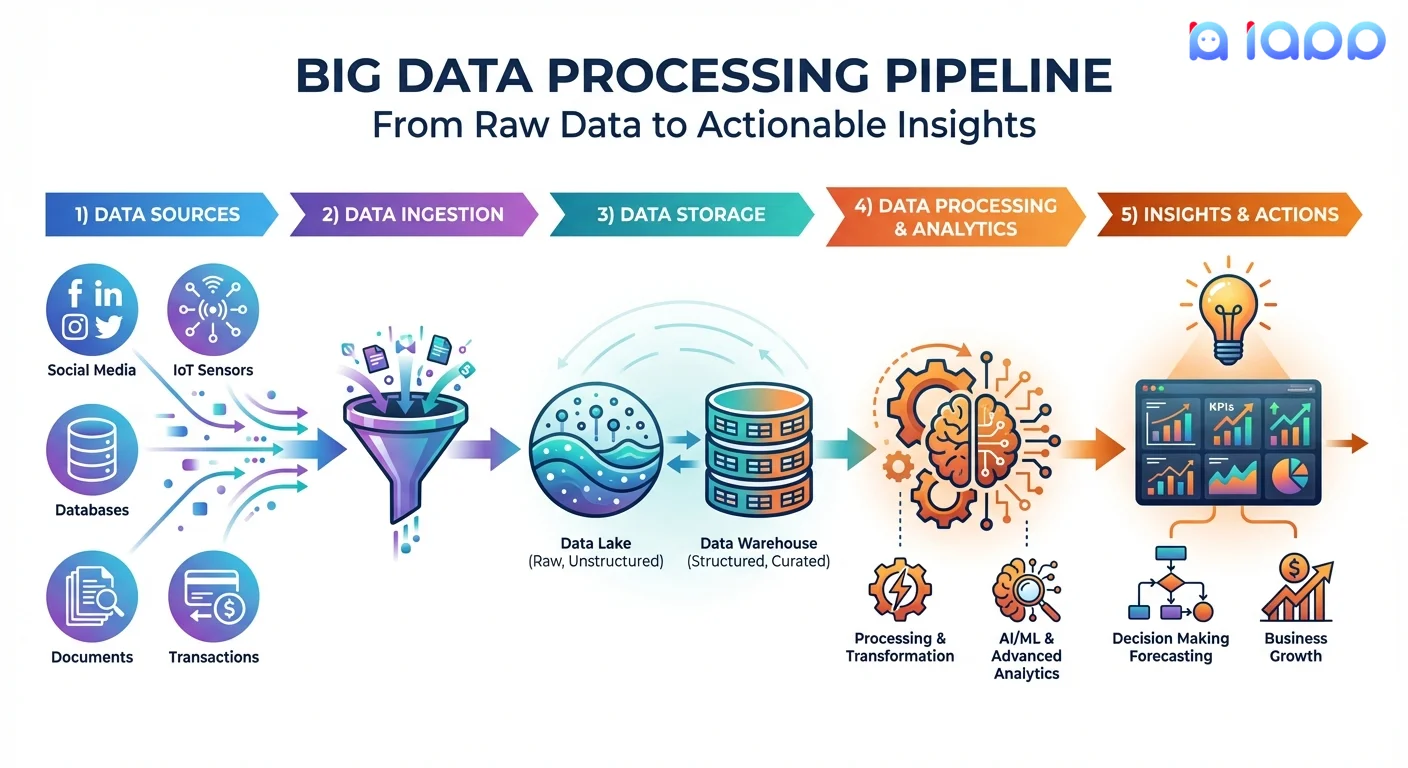
The Big Data Pipeline
-
Data Sources
- Internal: CRM, ERP, transactions, logs
- External: Social media, public data, third-party
- IoT: Sensors, devices, equipment
- User-generated: Documents, images, feedback
-
Data Ingestion
- Batch ingestion (periodic bulk loads)
- Stream ingestion (real-time continuous)
- API integrations
- File uploads and transfers
-
Data Storage
- Data lakes for raw data
- Data warehouses for processed data
- Distributed storage systems
- Cloud storage (scalable, cost-effective)
-
Data Processing
- Cleaning and validation
- Transformation and enrichment
- Aggregation and summarization
- Machine learning and AI analysis
-
Insights & Actions
- Dashboards and visualizations
- Reports and alerts
- Predictive models
- Automated decisions and actions
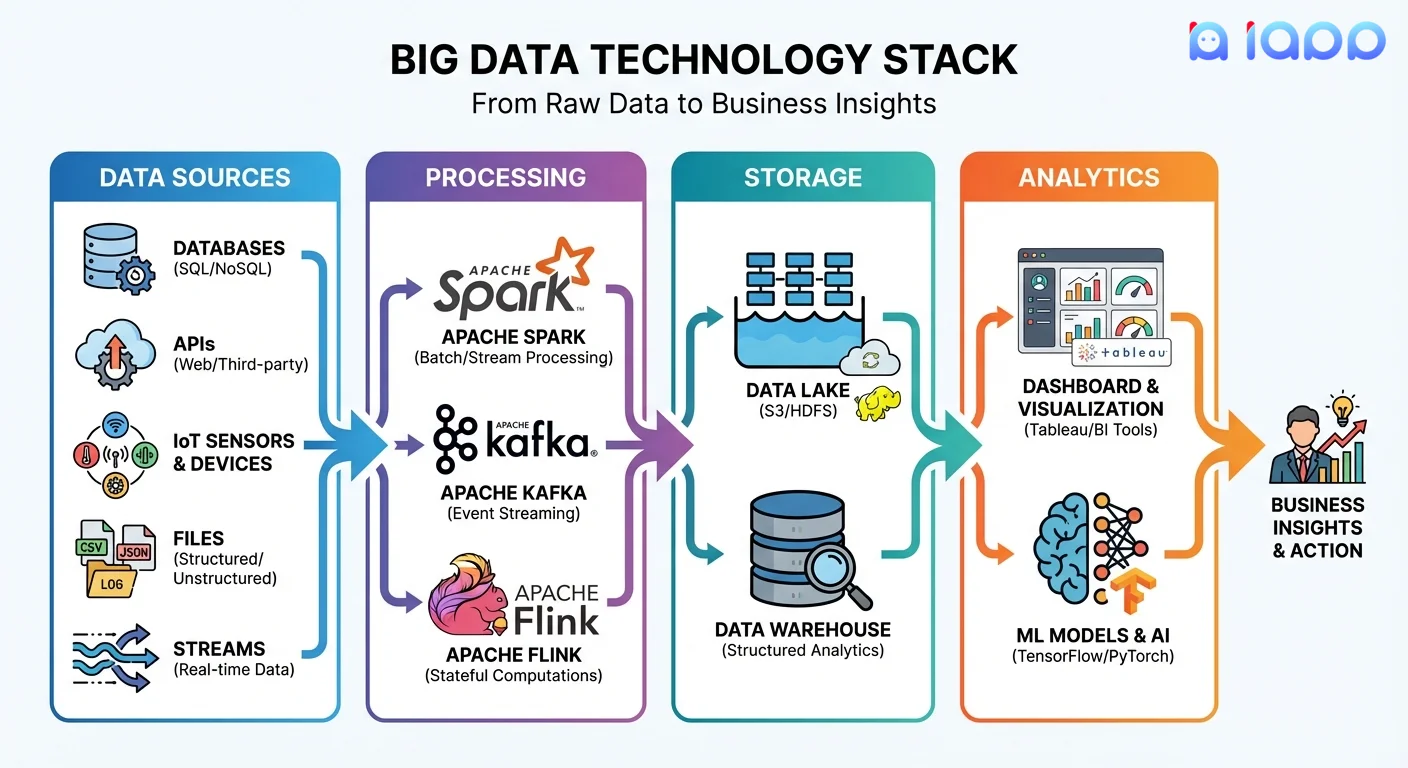
Technology Stack Example
Big Data in Thailand: Real Applications
1. Thai Document Processing at Scale
Using Thai OCR APIs:
- Process millions of Thai ID cards, passports, documents
- Extract structured data automatically
- Enable large-scale identity verification
- Build searchable document archives
2. Voice Data Analytics
Using Speech-to-Text:
- Transcribe thousands of call center recordings
- Analyze customer sentiment at scale
- Extract insights from voice data
- Build searchable audio archives
3. Thai Text Analytics
Using Chinda Thai LLM:
- Analyze millions of Thai social media posts
- Extract sentiment and topics
- Understand customer feedback at scale
- Generate insights from unstructured text
4. Multilingual Data Processing
Using Translation API:
- Process data in multiple languages
- Standardize multilingual content
- Enable cross-language analytics
- Reach international markets
5. Legal Document Analysis
Using Thanoy Legal AI:
- Analyze large volumes of legal documents
- Extract key clauses and terms
- Identify patterns across contracts
- Automate legal research
Building Big Data Solutions with iApp
iApp Technology provides AI APIs that transform unstructured data into structured insights:
Available Components
| Data Type | iApp Product | Big Data Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Thai Documents | Thai OCR APIs | Document digitization at scale |
| Thai Audio | Speech-to-Text | Voice data analytics |
| Thai Text | Chinda Thai LLM | Text analytics and NLP |
| Images/Faces | Face Recognition | Visual data processing |
| Multilingual | Translation API | Cross-language data |
| Legal Docs | Thanoy Legal AI | Legal document analysis |
Example: Document Processing Pipeline
import requests
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
def process_thai_document(document_path):
"""
Process a Thai document and extract structured data
"""
with open(document_path, 'rb') as f:
response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/thai-national-id-ocr/v3',
headers={'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY'},
files={'file': f}
)
return response.json()
def batch_process_documents(document_list):
"""
Process multiple documents in parallel for Big Data scale
"""
results = []
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10) as executor:
futures = [
executor.submit(process_thai_document, doc)
for doc in document_list
]
for future in futures:
results.append(future.result())
return results
# Example: Process 1000 documents
documents = ['doc1.jpg', 'doc2.jpg', ...] # Your document list
structured_data = batch_process_documents(documents)
# Now you have structured data ready for analytics!
# Store in database, data warehouse, or data lake
Example: Voice Analytics Pipeline
import requests
def transcribe_and_analyze(audio_file):
"""
Transcribe audio and analyze with LLM
"""
# Step 1: Transcribe Thai audio
with open(audio_file, 'rb') as f:
stt_response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/thai-speech-to-text/v2',
headers={'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY'},
files={'file': f}
)
transcript = stt_response.json()['transcript']
# Step 2: Analyze with LLM
analysis_response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/v3/llm/chinda-thaillm-4b/chat/completions',
headers={
'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
json={
'model': 'chinda-qwen3-4b',
'messages': [{
'role': 'user',
'content': f"""วิเคราะห์การสนทนานี้:
{transcript}
สรุป:
1. หัวข้อหลัก
2. ความรู้สึกของลูกค้า (บวก/ลบ/เป็นกลาง)
3. ประเด็นหรือข้อร้องเรียน
4. การดำเนินการที่แนะนำ"""
}],
'max_tokens': 512
}
)
return {
'transcript': transcript,
'analysis': analysis_response.json()['choices'][0]['message']['content']
}
Getting Started with Big Data
Step 1: Identify Your Data Sources
What data do you have?
- Customer transactions
- Website/app behavior
- Documents and files
- Call recordings
- Social media mentions
Step 2: Define Your Goals
What insights do you need?
- Customer understanding
- Operational efficiency
- Risk management
- Revenue optimization
Step 3: Start Small, Scale Up
Don't try to boil the ocean:
- Pick one use case
- Prove value with pilot
- Build on success
- Gradually expand
Step 4: Use AI to Unlock Unstructured Data
Transform raw data into insights:
- Use Thai OCR for documents
- Use Speech-to-Text for audio
- Use Chinda LLM for text analysis
Resources
- Get API Access: API Key Management
- Try Thai OCR: Document OCR Demo
- Try Speech APIs: Speech-to-Text Demo
- Explore All APIs: Complete API Catalog
- Join Community: Discord
The Future of Big Data
Trends to Watch
- AI-Powered Analytics: Machine learning making sense of complex data automatically
- Real-Time Everything: Instant insights instead of batch processing
- Edge Computing: Processing data closer to where it's generated
- Data Mesh: Decentralized data ownership and governance
- Privacy-Preserving Analytics: Deriving insights while protecting privacy
Why Thai Businesses Should Act Now
- Data is Growing: Thai digital economy generating more data than ever
- Competitive Pressure: Competitors are investing in data capabilities
- AI Accessibility: Tools like iApp APIs make AI analytics accessible
- Customer Expectations: Customers expect personalized, data-driven experiences
- Regulation Readiness: PDPA compliance requires understanding your data
Conclusion
Big Data isn't just about having lots of information — it's about transforming that information into actionable insights that drive better decisions. From understanding customers to optimizing operations, Big Data capabilities have become essential for competitive businesses.
The challenge for many Thai businesses is that much of their valuable data is locked in unstructured formats: Thai documents, voice recordings, images, and text. This is where iApp Technology's AI APIs shine — transforming unstructured Thai data into structured insights at scale.
With Thai OCR for document processing, Speech-to-Text for voice analytics, Chinda Thai LLM for text analysis, and Translation for multilingual data — Thai businesses have the tools to unlock the value in their Big Data.
Ready to transform your data into insights? Sign up for free and start processing Thai data at scale today!
Questions? Join our Discord Community or email us at support@iapp.co.th.
iApp Technology Co., Ltd. Thailand's Leading AI Technology Company