What is Machine Learning? A Complete Guide for Beginners
Every time Netflix recommends a movie you actually want to watch, or your email filters out spam automatically, or your phone recognizes your face to unlock — that's Machine Learning at work. It's the technology that enables computers to learn from experience rather than being explicitly programmed for every task. And it's revolutionizing virtually every industry.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed. Instead of writing rules for every scenario, we feed the machine data and let it discover patterns on its own.
Think of it this way:
- Traditional Programming: Human writes rules → Computer follows rules → Output
- Machine Learning: Human provides data → Computer learns patterns → Computer creates rules → Output
At its core, machine learning:
- Learns patterns from historical data
- Improves performance with more experience
- Predicts outcomes for new, unseen data
- Adapts to changing conditions automatically
Simple Example
Traditional Programming:
IF email contains "free money" AND sender is unknown
THEN mark as spam
(You must write rules for every spam pattern — impossible to cover all cases!)
Machine Learning:
Training: Show the model 10,000 spam emails and 10,000 normal emails
Result: Model learns what spam "looks like"
Usage: Model automatically detects new spam patterns you never programmed
Types of Machine Learning
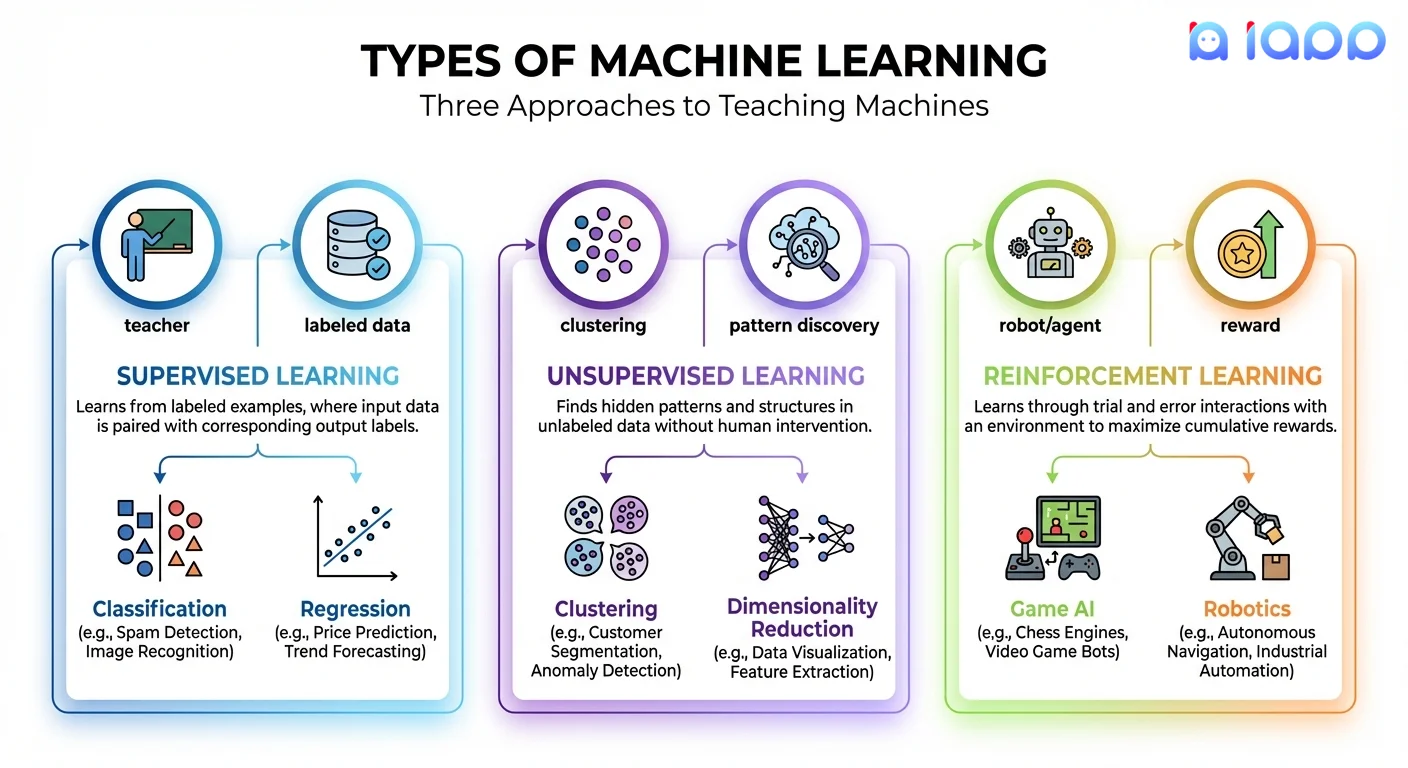
1. Supervised Learning
The model learns from labeled data — examples where we know the correct answer.
How it works:
- Training data includes inputs AND correct outputs
- Model learns the relationship between them
- Model can then predict outputs for new inputs
Types:
- Classification: Predict categories (spam/not spam, cat/dog, fraud/legitimate)
- Regression: Predict numbers (price, temperature, sales volume)
Examples:
- Email spam detection
- Credit score prediction
- Medical diagnosis
- Image recognition
Best for: Problems where you have historical data with known outcomes
2. Unsupervised Learning
The model finds hidden patterns in data without being told what to look for.
How it works:
- Training data has NO labels
- Model discovers structure on its own
- Finds groups, patterns, or anomalies
Types:
- Clustering: Group similar items (customer segments, document topics)
- Dimensionality Reduction: Simplify complex data while preserving important features
- Anomaly Detection: Find unusual patterns (fraud, defects)
Examples:
- Customer segmentation
- Recommendation systems
- Anomaly detection
- Market basket analysis
Best for: Exploration, finding structure in data, when you don't know what to look for
3. Reinforcement Learning
The model learns through trial and error, receiving rewards for good actions.
How it works:
- Agent takes actions in an environment
- Receives rewards or penalties
- Learns to maximize total reward over time
Components:
- Agent: The learner/decision maker
- Environment: What the agent interacts with
- Actions: What the agent can do
- Rewards: Feedback signals
Examples:
- Game AI (AlphaGo, chess engines)
- Robotics control
- Autonomous vehicles
- Resource optimization
Best for: Sequential decision-making, control problems, games
Key Machine Learning Terms Explained (Jargon Buster)
1. Model
What it is: The mathematical representation that the machine learning algorithm produces after training.
Simple analogy: Like a student's brain after studying — it has "learned" patterns and can now answer questions about new examples.
In practice: A trained model is a file that contains the learned patterns and can make predictions on new data.
2. Training
What it is: The process of feeding data to an algorithm so it can learn patterns.
Simple analogy: Like teaching a child to recognize animals by showing them many pictures with labels.
Process:
- Feed training data to algorithm
- Algorithm adjusts its internal parameters
- Repeat until accuracy is satisfactory
- Result: A trained model
3. Features
What it is: The input variables or attributes used to make predictions.
Simple analogy: When you describe a house to predict its price, features might be: square meters, number of bedrooms, location, age.
Example:
- For spam detection: sender, subject keywords, links count, time sent
- For face recognition: pixel values, edge patterns, facial landmarks
4. Overfitting vs Underfitting
Overfitting: Model memorizes training data but fails on new data (too complex)
- Like a student who memorizes exam answers but can't solve new problems
Underfitting: Model is too simple to capture patterns (too basic)
- Like a student who didn't study enough and can't answer any questions
Goal: Find the sweet spot where model generalizes well to new data
5. Neural Network / Deep Learning
What it is: A type of ML model inspired by the human brain, with layers of interconnected "neurons."
Simple analogy: Like a team of specialists — each layer extracts different levels of understanding, from simple features to complex concepts.
Deep Learning: Neural networks with many layers — "deep" refers to the depth of layers.
Powers: Image recognition, speech recognition, language translation, generative AI
Why Machine Learning Matters
1. Automation of Complex Tasks
ML can automate tasks that are too complex to program with traditional rules:
- Understanding human language
- Recognizing images and faces
- Predicting complex outcomes
2. Continuous Improvement
Unlike static programs, ML models can:
- Improve with more data
- Adapt to changing patterns
- Get smarter over time
3. Handling Scale
ML processes vast amounts of data that humans couldn't analyze:
- Millions of transactions
- Billions of user interactions
- Real-time streaming data
4. Personalization
ML enables personalized experiences at scale:
- Product recommendations
- Content curation
- Targeted advertising
5. Discovery
ML finds patterns humans might miss:
- Medical research breakthroughs
- Scientific discoveries
- Business insights
What Problems Does Machine Learning Solve?
| Problem | Traditional Approach | Machine Learning Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Spam detection | Manual rules | Learns patterns automatically |
| Fraud detection | Fixed thresholds | Adapts to new fraud patterns |
| Customer churn | Gut feeling | Predicts who will leave |
| Image classification | Impossible | Recognizes objects, faces, text |
| Language translation | Dictionary lookup | Understands context and nuance |
| Recommendations | Basic filtering | Personalized suggestions |
| Demand forecasting | Historical averages | Accurate predictions |
How Machine Learning Works
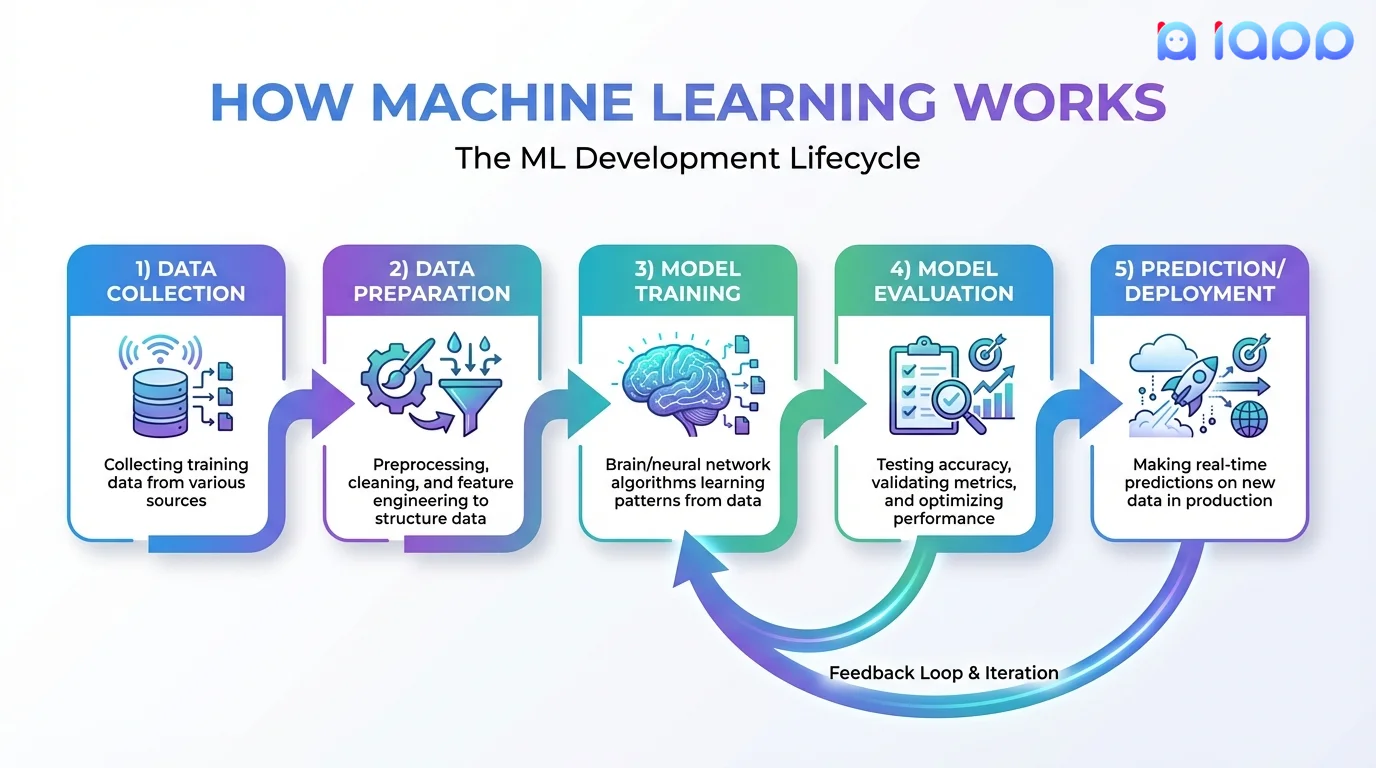
The ML Development Lifecycle
-
Data Collection
- Gather relevant training data
- More data generally = better models
- Quality matters as much as quantity
-
Data Preparation
- Clean and preprocess data
- Handle missing values
- Feature engineering (create useful inputs)
- Split into training and testing sets
-
Model Training
- Choose appropriate algorithm
- Feed training data to model
- Model learns patterns iteratively
- Adjust parameters for best performance
-
Model Evaluation
- Test on held-out data
- Measure accuracy, precision, recall
- Check for overfitting/underfitting
- Compare different models
-
Deployment & Prediction
- Deploy model to production
- Make predictions on new data
- Monitor performance
- Retrain as needed
Example: Thai ID Card OCR
Problem: Extract text from Thai ID card images
Training Phase:
1. Collect: 100,000 Thai ID card images with labeled text
2. Prepare: Crop, resize, augment images
3. Train: CNN learns to recognize Thai characters
4. Evaluate: 99.5% accuracy on test set
5. Deploy: API ready for production
Inference (Usage):
Input: New Thai ID card image
↓
Model processes image
↓
Output: {"name": "สมชาย ใจดี", "id": "1-2345-67890-12-3", ...}
Machine Learning in Thailand: Real Applications
1. Thai OCR & Document Processing
Using Thai OCR APIs:
- ML models trained on millions of Thai documents
- Recognizes Thai script with high accuracy
- Extracts structured data from ID cards, passports, documents
- Handles various fonts, handwriting, and conditions
2. Thai Speech Recognition
Using Speech-to-Text:
- Deep learning models trained on Thai speech
- Understands various accents and dialects
- Handles background noise and multiple speakers
- Real-time transcription capabilities
3. Thai Natural Language Processing
Using Chinda Thai LLM:
- Large language model trained on Thai text
- Understands Thai grammar and context
- Generates natural Thai responses
- Powers chatbots and text analysis
4. Face Recognition & Verification
Using Face Recognition:
- Deep learning for face detection and matching
- Works across different angles and lighting
- Liveness detection to prevent spoofing
- Bank-grade accuracy and security
5. Translation
Using Translation API:
- Neural machine translation
- Preserves context and meaning
- Supports Thai, English, Chinese, Japanese
- Handles idioms and cultural expressions
Building with iApp's ML-Powered APIs
iApp Technology provides pre-trained ML models as easy-to-use APIs:
Available ML Services
| ML Task | iApp Product | Model Type |
|---|---|---|
| Thai OCR | Thai OCR APIs | CNN + Transformer |
| Speech Recognition | Speech-to-Text | Deep Neural Network |
| Face Recognition | Face Recognition | Deep CNN |
| Thai Language | Chinda Thai LLM | Large Language Model |
| Translation | Translation API | Neural MT |
| Text-to-Speech | Text-to-Speech | Neural TTS |
Example: Using ML for Thai Document Processing
import requests
def process_document_with_ml(image_path):
"""
Use iApp's ML-powered OCR to extract data from Thai documents
"""
with open(image_path, 'rb') as f:
response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/thai-national-id-ocr/v3',
headers={'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY'},
files={'file': f}
)
result = response.json()
# ML model has extracted structured data
return {
'name_th': result.get('name_th'),
'name_en': result.get('name_en'),
'id_number': result.get('id_number'),
'date_of_birth': result.get('date_of_birth'),
'address': result.get('address'),
'confidence': result.get('confidence')
}
# Example usage
data = process_document_with_ml('thai_id_card.jpg')
print(f"Extracted name: {data['name_th']}")
print(f"Confidence: {data['confidence']}")
Example: ML-Powered Thai Text Analysis
import requests
def analyze_thai_text(text):
"""
Use Chinda LLM to analyze Thai text
"""
response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/v3/llm/chinda-thaillm-4b/chat/completions',
headers={
'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
json={
'model': 'chinda-qwen3-4b',
'messages': [{
'role': 'user',
'content': f"""วิเคราะห์ข้อความต่อไปนี้:
"{text}"
กรุณาสรุป:
1. ความรู้สึก (บวก/ลบ/เป�็นกลาง)
2. หัวข้อหลัก
3. ประเด็นสำคัญ"""
}],
'max_tokens': 512
}
)
return response.json()['choices'][0]['message']['content']
# Example usage
result = analyze_thai_text("สินค้าคุณภาพดีมาก ส่งเร็ว แพคอย่างดี จะกลับมาซื้ออีก")
print(result)
Getting Started with Machine Learning
For Business Users
You don't need to build ML models from scratch! Use pre-trained models via APIs:
- Identify your use case: Document processing? Speech? Face recognition?
- Choose the right API: Browse iApp's API catalog
- Get your API key: Sign up for free
- Integrate: Simple REST API calls from any language
- Scale: Pay only for what you use
For Developers & Data Scientists
Want to understand ML deeper?
- Learn the fundamentals: Linear regression, decision trees, neural networks
- Practice with data: Kaggle competitions, public datasets
- Use frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn
- Start simple: Begin with supervised learning classification
- Build projects: Apply ML to real problems
Resources
- Get API Access: API Key Management
- Try Thai OCR: Document OCR Demo
- Try Speech AI: Speech-to-Text Demo
- Try Thai LLM: Chinda Demo
- Join Community: Discord
The Future of Machine Learning
Trends to Watch
- Foundation Models: Large pre-trained models that can be adapted to many tasks
- AutoML: Automated machine learning reducing need for expertise
- Edge ML: Running models on devices instead of cloud
- Multimodal ML: Models that understand text, images, audio together
- Responsible AI: Focus on fairness, transparency, and privacy
Why Thai Businesses Should Leverage ML Now
- Competitive Edge: ML-powered automation and insights
- Cost Reduction: Automate manual, repetitive tasks
- Better Decisions: Data-driven instead of gut-feeling
- Customer Experience: Personalization and faster service
- Innovation: New products and services enabled by ML
Conclusion
Machine Learning is the technology that enables computers to learn from data and improve over time. From recognizing Thai text to understanding speech to detecting fraud, ML powers the intelligent applications that are transforming every industry.
The good news? You don't need a PhD in machine learning to benefit from it. iApp Technology provides pre-trained ML models as simple APIs — Thai OCR for document processing, Speech-to-Text for voice, Face Recognition for identity verification, and Chinda Thai LLM for Thai language understanding.
Ready to add machine learning to your applications? Sign up for free and start using our ML-powered APIs today!
Questions? Join our Discord Community or email us at support@iapp.co.th.
iApp Technology Co., Ltd. Thailand's Leading AI Technology Company