What is Deep Learning? A Complete Guide for Beginners
When your phone recognizes your face in a split second, when Google Translate converts Thai to English almost perfectly, or when ChatGPT generates human-like responses — that's Deep Learning at work. It's the technology behind virtually every major AI breakthrough of the last decade, and it's transforming what computers can do.
What is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers to learn from large amounts of data. The "deep" in deep learning refers to the depth of layers in these neural networks — from simple 3-layer networks to massive models with hundreds of layers.
Think of it this way:
- Traditional Programming: Human writes explicit rules
- Machine Learning: Computer learns patterns from data
- Deep Learning: Computer learns complex patterns through multiple layers of abstraction
At its core, deep learning:
- Learns hierarchical representations from raw data
- Discovers features automatically (no manual feature engineering)
- Handles unstructured data like images, audio, and text
- Scales with more data and computing power
Simple Analogy
Imagine teaching a child to recognize a cat:
- Traditional Programming: List every rule (has fur, four legs, pointy ears, whiskers...)
- Machine Learning: Show examples and let the child find patterns
- Deep Learning: The child first learns edges → then shapes → then body parts → then the whole cat
Each layer builds on the previous one, learning increasingly abstract concepts.
How Deep Learning Works
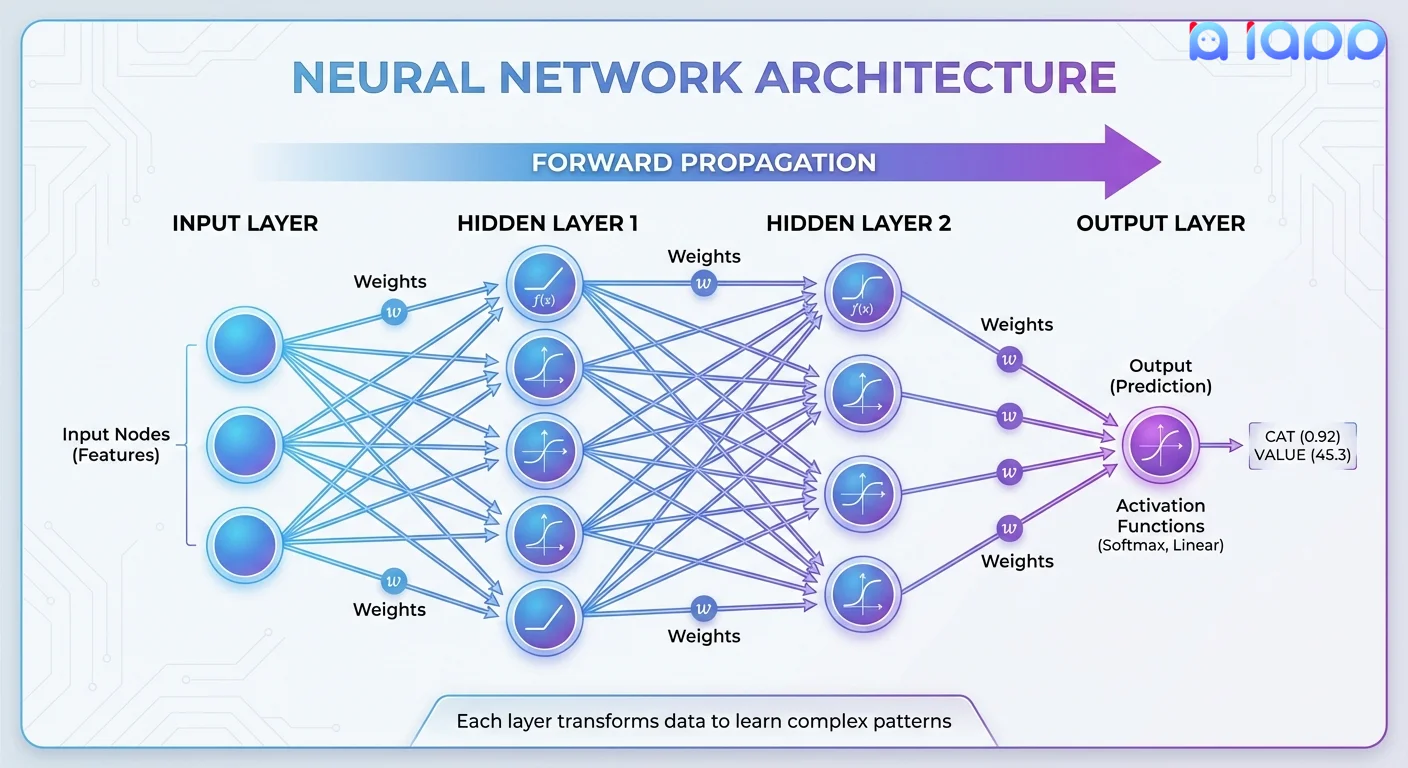
The Neural Network Structure
1. Input Layer
- Receives raw data (pixels, words, numbers)
- Each node represents one feature or input value
2. Hidden Layers (The "Deep" Part)
- Multiple layers that transform data
- Each layer learns different levels of abstraction
- More layers = deeper network = more complex patterns
3. Output Layer
- Produces the final prediction
- Could be a class label, probability, or generated content
The Learning Process
Step 1: Forward Propagation
Data flows from input → through hidden layers → to output
Each neuron applies: output = activation(weights × inputs + bias)
Step 2: Calculate Loss
Compare prediction to actual answer
Loss = how wrong the prediction was
Step 3: Backpropagation
Calculate how each weight contributed to the error
Propagate error backwards through the network
Step 4: Update Weights
Adjust weights to reduce error
Use optimization algorithms like SGD or Adam
Step 5: Repeat
Train on thousands/millions of examples
Until model converges to good accuracy
Types of Deep Learning Architectures
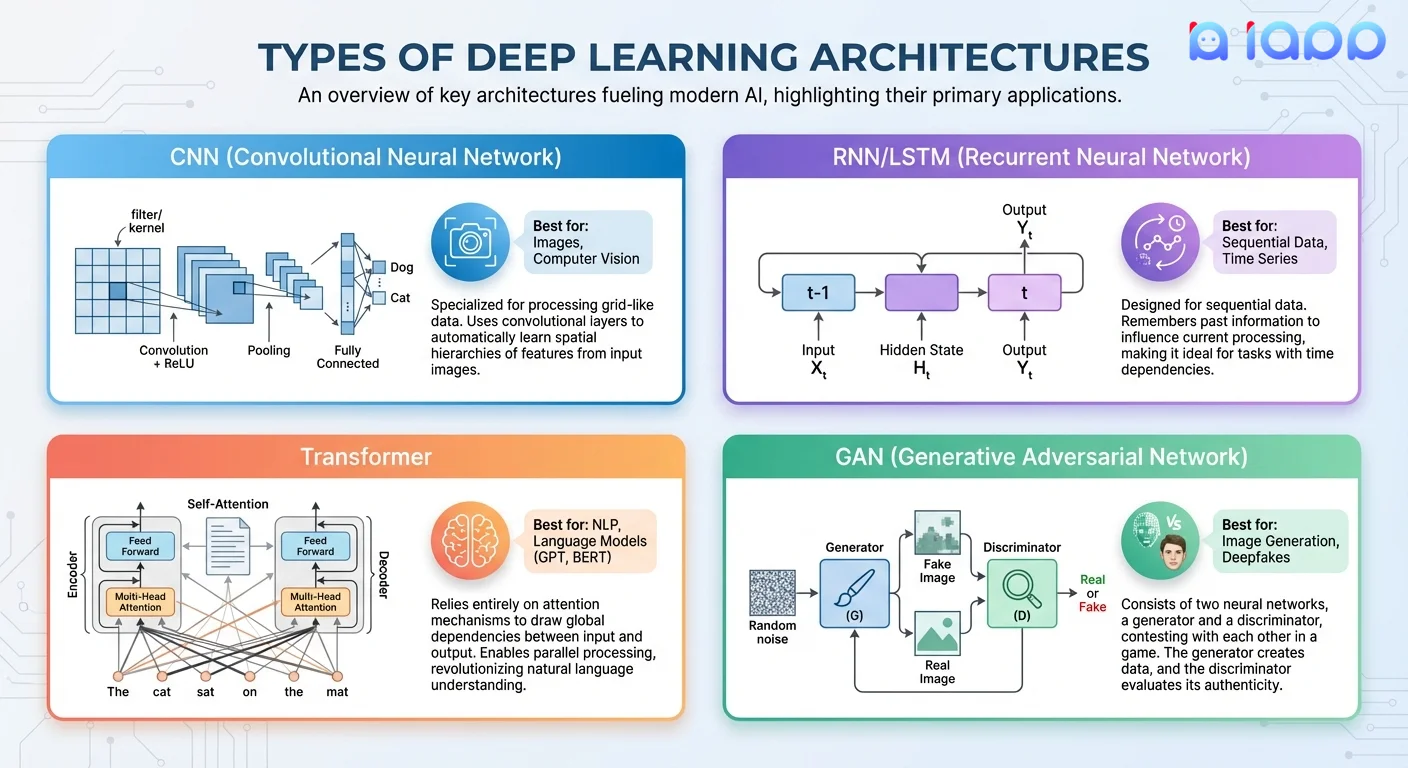
1. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
Best for: Images, video, computer vision tasks
How it works:
- Uses convolutional filters to detect patterns
- Learns edges → textures → shapes → objects
- Preserves spatial relationships in data
Applications:
- Image classification (cat vs dog)
- Object detection (finding faces in photos)
- OCR (reading text from images)
- Medical image analysis
Used in: iApp's Thai OCR, Face Recognition
2. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN/LSTM)
Best for: Sequential data, time series, speech
How it works:
- Has "memory" of previous inputs
- Processes sequences one element at a time
- LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) solves vanishing gradient problem
Applications:
- Speech recognition
- Language modeling
- Time series prediction
- Music generation
Used in: iApp's Speech-to-Text
3. Transformers
Best for: Natural language processing, modern LLMs
How it works:
- Uses "attention" mechanism to weigh importance of all inputs
- Processes entire sequences in parallel (faster than RNN)
- Self-attention captures long-range dependencies
Applications:
- Language models (GPT, BERT, LLaMA)
- Machine translation
- Text generation
- Question answering
Used in: iApp's Chinda Thai LLM, Translation API
4. Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN)
Best for: Generating new content, image synthesis
How it works:
- Two networks compete: Generator vs Discriminator
- Generator creates fake data; Discriminator tries to detect fakes
- Competition improves both until Generator creates realistic outputs
Applications:
- Image generation
- Style transfer
- Data augmentation
- Deepfakes
5. Autoencoders
Best for: Compression, anomaly detection, denoising
How it works:
- Encoder compresses data to smaller representation
- Decoder reconstructs original from compressed form
- Forces network to learn essential features
Applications:
- Dimensionality reduction
- Anomaly detection
- Image denoising
- Feature learning
Key Deep Learning Terms Explained (Jargon Buster)
1. Neuron (Node)
What it is: The basic computational unit in a neural network that receives inputs, applies weights and a function, then outputs a value.
Simple analogy: Like a brain cell that fires when it receives enough signals from connected cells.
Formula: output = activation(sum(weights × inputs) + bias)
2. Activation Function
What it is: A mathematical function that determines whether a neuron should "fire" and how strongly.
Common types:
- ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit):
max(0, x)— Simple, fast, most popular - Sigmoid: Squashes output to 0-1 — Good for probabilities
- Softmax: Outputs probability distribution — Used for classification
- Tanh: Squashes to -1 to 1 — Better than sigmoid for hidden layers
Why it matters: Without activation functions, no matter how many layers, the network would only compute linear functions. Activations add non-linearity, enabling learning of complex patterns.
3. Backpropagation
What it is: The algorithm that calculates how much each weight contributed to the prediction error, then updates weights to reduce future errors.
Simple analogy: Like tracing back through a recipe to figure out which ingredient caused a dish to taste wrong, then adjusting the amounts.
Process:
- Calculate error at output
- Propagate error backward through layers
- Calculate gradient (direction to adjust) for each weight
- Update weights using gradient descent
4. Epoch, Batch, Iteration
Epoch: One complete pass through the entire training dataset
- Training typically requires many epochs (10-100+)
Batch: A subset of training data processed together
- Batch size typically 32, 64, 128, or 256 samples
Iteration: One update of the model's weights
- Iterations per epoch = dataset size ÷ batch size
Example: 10,000 training samples, batch size 100
- 1 epoch = 100 iterations
- 50 epochs = 5,000 iterations
5. Overfitting vs Underfitting (in Deep Learning Context)
Overfitting: Network memorizes training data but fails on new data
- Signs: Training accuracy high, validation accuracy low
- Solutions: Dropout, regularization, more data, data augmentation, early stopping
Underfitting: Network too simple to capture patterns
- Signs: Both training and validation accuracy low
- Solutions: More layers, more neurons, longer training, better architecture
Dropout: Randomly "turning off" neurons during training to prevent overfitting — like training a team where different members are absent each practice, forcing everyone to be capable.
Why Deep Learning Matters
1. Automatic Feature Learning
Unlike traditional ML, deep learning discovers relevant features on its own:
- No manual feature engineering
- Finds patterns humans might miss
- Works with raw, unstructured data
2. Unprecedented Accuracy
Deep learning has achieved human-level (or better) performance in:
- Image recognition (ImageNet)
- Speech recognition (voice assistants)
- Game playing (AlphaGo, chess)
- Language understanding (GPT-4)
3. Handles Complex Data
Excels at processing:
- Images and video
- Natural language
- Speech and audio
- Multi-modal combinations
4. Scales with Data and Compute
More data + more computing power = better results
- Larger models learn more complex patterns
- Performance continues to improve with scale
5. Transfer Learning
Pre-trained models can be fine-tuned for new tasks:
- Don't need to train from scratch
- Less data required for new applications
- Faster development time
What Problems Does Deep Learning Solve?
| Problem | Traditional Approach | Deep Learning Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Image recognition | Hand-crafted features + classifier | CNN learns features automatically |
| Speech recognition | Acoustic models + language models | End-to-end neural networks |
| Machine translation | Rule-based or statistical MT | Neural MT with Transformers |
| Face recognition | Manual feature extraction | Deep CNNs with embeddings |
| Text generation | Templates or Markov chains | Large Language Models |
| Game playing | Hard-coded strategies | Reinforcement learning + neural nets |
Deep Learning in Thailand: Real Applications
1. Thai Document OCR
Using Thai OCR APIs:
- Deep CNNs trained on millions of Thai documents
- Recognizes Thai script, handwriting, and various fonts
- Extracts structured data from ID cards, passports, receipts
- Powers eKYC for Thai banks and fintech
2. Thai Speech Recognition
Using Speech-to-Text:
- Deep neural networks trained on Thai speech data
- Handles tones, regional accents, and dialects
- Real-time transcription capabilities
- Powers voice assistants and call center automation
3. Thai Language Understanding
Using Chinda Thai LLM:
- Transformer-based large language model
- Trained on Thai text corpus
- Understands context, grammar, and nuance
- Powers chatbots, content generation, and text analysis
4. Face Recognition & Verification
Using Face Recognition:
- Deep CNNs for face detection and embedding
- Liveness detection to prevent spoofing
- Works across different angles, lighting, and ages
- Bank-grade security for identity verification
5. Neural Machine Translation
Using Translation API:
- Transformer models for Thai-English-Chinese translation
- Preserves context and meaning
- Handles idioms and cultural expressions
- Real-time translation capabilities
Building with iApp's Deep Learning APIs
iApp Technology provides pre-trained deep learning models as easy-to-use APIs:
Available Deep Learning Services
| Deep Learning Task | iApp Product | Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Thai OCR | Thai OCR APIs | CNN + Transformer |
| Speech Recognition | Speech-to-Text | Deep Neural Network |
| Face Recognition | Face Recognition | Deep CNN |
| Thai Language | Chinda Thai LLM | Transformer (LLM) |
| Translation | Translation API | Neural MT |
| Text-to-Speech | Text-to-Speech | Neural TTS |
Example: Using Deep Learning for Thai OCR
import requests
def extract_text_with_deep_learning(image_path):
"""
Use iApp's deep learning OCR to extract text from Thai documents
"""
with open(image_path, 'rb') as f:
response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/thai-national-id-ocr/v3',
headers={'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY'},
files={'file': f}
)
result = response.json()
# Deep learning model has extracted structured data
return {
'name_th': result.get('name_th'),
'name_en': result.get('name_en'),
'id_number': result.get('id_number'),
'date_of_birth': result.get('date_of_birth'),
'confidence': result.get('confidence')
}
# Example usage
data = extract_text_with_deep_learning('thai_id_card.jpg')
print(f"Extracted name: {data['name_th']}")
print(f"Confidence: {data['confidence']}")
Example: Deep Learning for Thai Text Generation
import requests
def generate_with_thai_llm(prompt):
"""
Use Chinda Thai LLM (Transformer-based) for text generation
"""
response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/v3/llm/chinda-thaillm-4b/chat/completions',
headers={
'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
json={
'model': 'chinda-qwen3-4b',
'messages': [{
'role': 'user',
'content': prompt
}],
'max_tokens': 512
}
)
return response.json()['choices'][0]['message']['content']
# Example usage
result = generate_with_thai_llm("อธิบายว่า Deep Learning คืออะไร ใน 3 ประโยค")
print(result)
Getting Started with Deep Learning
For Business Users
You don't need to build deep learning models from scratch! Use pre-trained models via APIs:
- Identify your use case: Document processing? Speech? Face recognition? Text generation?
- Choose the right API: Browse iApp's API catalog
- Get your API key: Sign up for free
- Integrate: Simple REST API calls from any language
- Scale: Pay only for what you use
For Developers & Data Scientists
Want to understand deep learning deeper?
- Learn the fundamentals: Start with basic neural networks, then CNNs, RNNs, Transformers
- Practice with frameworks: TensorFlow, PyTorch, Keras
- Take courses: Fast.ai, Coursera Deep Learning Specialization, Stanford CS231n
- Build projects: Apply deep learning to real problems
- Use pre-trained models: Hugging Face, TensorFlow Hub, PyTorch Hub
Resources
- Get API Access: API Key Management
- Try Thai OCR: Document OCR Demo
- Try Speech AI: Speech-to-Text Demo
- Try Thai LLM: Chinda Demo
- Join Community: Discord
The Future of Deep Learning
Trends to Watch
- Foundation Models: Large pre-trained models (GPT-4, Claude, Gemini) as base for many applications
- Multimodal Models: Single models understanding text, images, audio, video together
- Efficient AI: Smaller, faster models for edge devices (mobile, IoT)
- AI Agents: Deep learning powering autonomous decision-making systems
- Responsible AI: Focus on fairness, interpretability, and safety
Why Thai Businesses Should Leverage Deep Learning Now
- Competitive Edge: AI-powered automation and insights
- Cost Reduction: Automate manual, repetitive tasks
- Better Customer Experience: Personalization and faster service
- Innovation: New products and services enabled by deep learning
- Global Standards: Thai-specific models rivaling international quality
Conclusion
Deep Learning is the breakthrough technology that powers modern AI — from recognizing faces to understanding language to generating content. By using multiple layers of neural networks, deep learning can automatically learn complex patterns from raw data, achieving superhuman performance in many tasks.
The good news? You don't need a PhD or expensive infrastructure to benefit from deep learning. iApp Technology provides pre-trained deep learning models as simple APIs — Thai OCR for document processing, Speech-to-Text for voice, Face Recognition for identity verification, and Chinda Thai LLM for Thai language understanding.
Ready to add deep learning to your applications? Sign up for free and start using our AI-powered APIs today!
Questions? Join our Discord Community or email us at support@iapp.co.th.
iApp Technology Co., Ltd. Thailand's Leading AI Technology Company