What is a Small Language Model (SLM)? A Beginner's Complete Guide
Everyone talks about Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 and Claude. But there's a growing movement toward their smaller, more efficient cousins: Small Language Models (SLMs). These compact AI models are revolutionizing how we deploy AI in real-world applications. Let's explore what they are and why they matter.
What is a Small Language Model (SLM)?
A Small Language Model (SLM) is a language model with significantly fewer parameters than large models - typically ranging from 1 billion to 10 billion parameters. Despite their smaller size, SLMs are designed to perform specific tasks efficiently while requiring less computational resources.
Think of it like this: An LLM is like a Swiss Army knife with 100 tools - powerful but bulky. An SLM is like a precision screwdriver - focused, efficient, and perfect for specific jobs.
Key Characteristics of SLMs
| Feature | Small Language Model (SLM) | Large Language Model (LLM) |
|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 1B - 10B | 70B - 1T+ |
| Memory Required | 2-16 GB | 100GB+ |
| Speed | Fast (milliseconds) | Slower (seconds) |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Deployment | On-device, Edge | Cloud-based |
| Specialization | Task-specific | General-purpose |
SLM vs LLM: Understanding the Difference
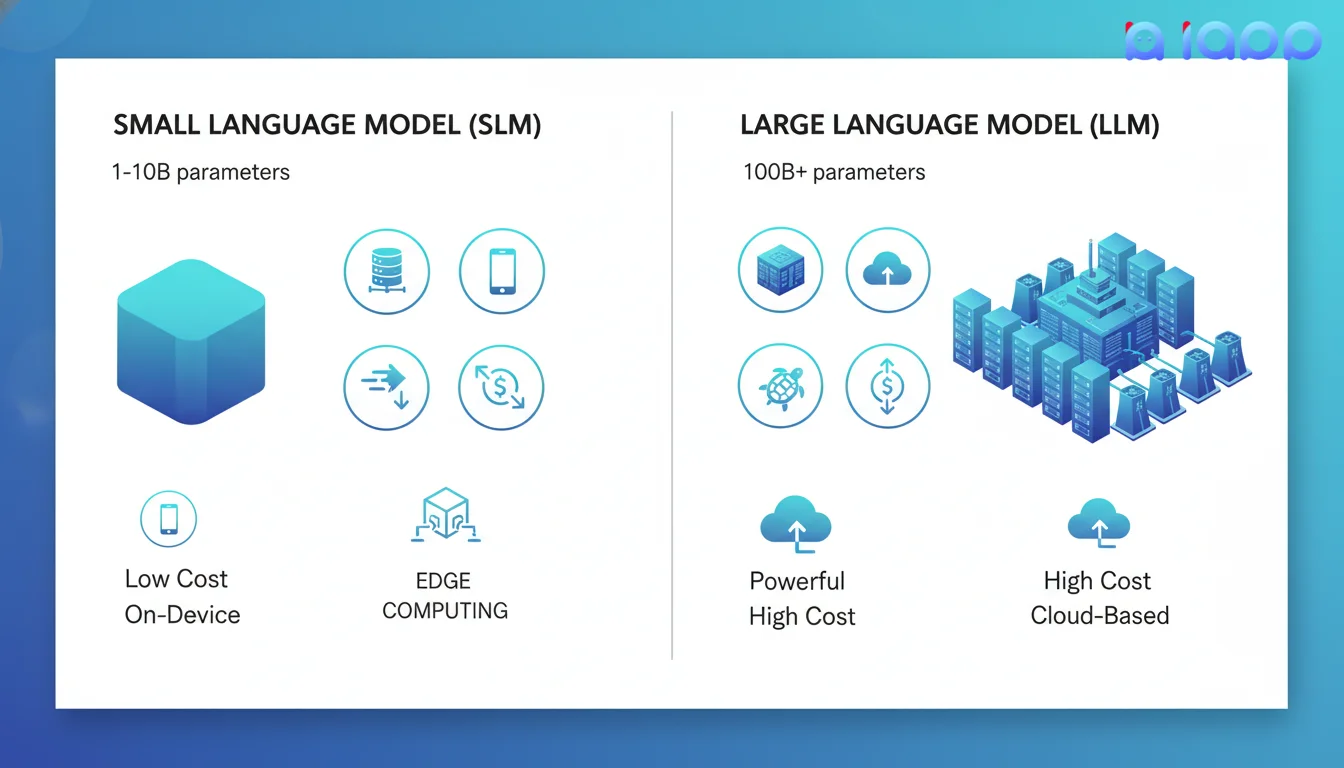
When to Use SLM vs LLM
Choose SLM when:
- Speed is critical (real-time responses)
- Running on devices with limited resources
- Privacy is paramount (data stays on-device)
- Cost optimization is needed
- Performing specific, well-defined tasks
Choose LLM when:
- Complex reasoning is required
- Multi-step problem solving
- Creative writing and brainstorming
- General-purpose assistance
- Handling diverse, unpredictable queries
Types of Small Language Models
1. General-Purpose SLMs
Compact models that can handle various tasks reasonably well.
- Examples: Phi-3, Gemma 2B, Llama 3.2 1B
- Use cases: Chatbots, text summarization, simple Q&A
2. Domain-Specific SLMs
Models fine-tuned for specific industries or tasks.
- Examples: Chinda Thai LLM (Thai language), CodeGemma (coding)
- Use cases: Thai customer service, code completion, medical triage
3. Distilled Models
Smaller models trained to mimic larger models' behavior.
- Examples: DistilBERT, TinyLlama
- Use cases: Fast inference, mobile deployment
4. Quantized Models
Full-size models compressed to run efficiently.
- Examples: GGUF format models, 4-bit quantized versions
- Use cases: Local deployment, edge devices
5. Multimodal SLMs
Small models that handle text plus other modalities.
- Examples: PaliGemma, LLaVA-Phi
- Use cases: Image captioning, visual Q&A on mobile
5 Use Cases for Small Language Models
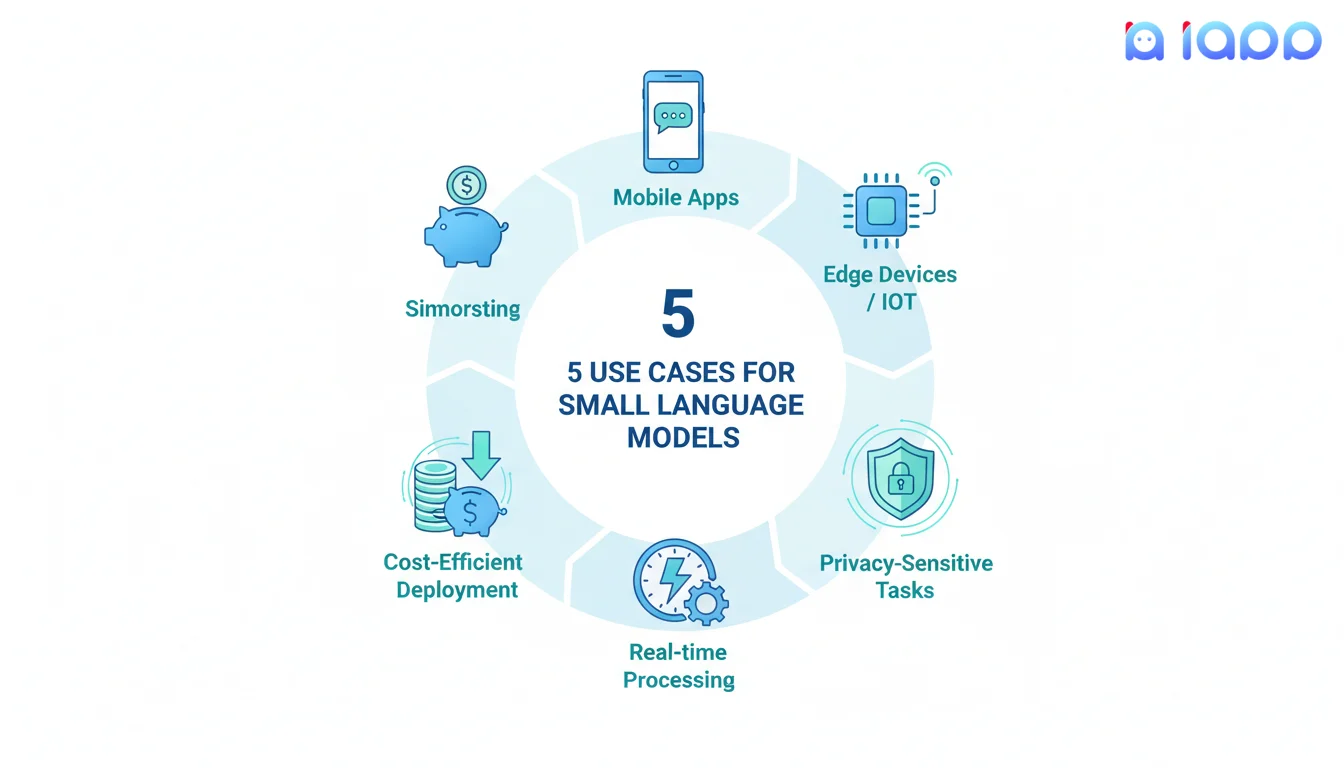
1. Mobile Applications
Run AI directly on smartphones without internet.
- Example: On-device text prediction, smart compose
- Benefit: Works offline, instant responses
2. Edge Devices & IoT
Deploy AI on sensors, cameras, and embedded systems.
- Example: Smart home voice assistant, industrial monitoring
- Benefit: No cloud latency, local processing
3. Privacy-Sensitive Tasks
Keep data on-premise for compliance and security.
- Example: Healthcare chatbots, financial document analysis
- Benefit: Data never leaves the device
4. Real-Time Processing
Get instant responses for time-critical applications.
- Example: Live translation, real-time transcription
- Benefit: Millisecond response times
5. Cost-Efficient Deployment
Scale AI without massive cloud bills.
- Example: Customer service automation for SMEs
- Benefit: 10-100x cost reduction vs cloud LLMs
Key AI Terms Explained (Jargon Buster)
1. Parameters
What it is: The "knowledge" stored in a model - numbers that determine how the model responds.
Simple analogy: Think of parameters like brain cells. More cells can store more information, but also require more energy.
Why it matters: SLMs have 1-10B parameters vs LLMs with 70B-1T+ parameters.
2. Quantization
What it is: Compressing a model by reducing the precision of its parameters (e.g., from 32-bit to 4-bit numbers).
Simple analogy: Like compressing a photo from RAW to JPEG - smaller file, slightly less detail, but still useful.
Why it matters: A 7B model normally needs 14GB RAM. Quantized to 4-bit, it needs only 4GB.
3. Distillation
What it is: Training a small model to mimic a larger model's behavior.
Simple analogy: A student (SLM) learning from a master teacher (LLM) - capturing the essence without needing the same resources.
Why it matters: Creates efficient models that retain much of the original's capability.
4. Edge Computing
What it is: Processing data locally on devices instead of sending to the cloud.
Simple analogy: Cooking at home vs ordering delivery - faster, more private, but limited menu options.
Why it matters: SLMs enable AI at the edge - on phones, cameras, and IoT devices.
5. Inference
What it is: The process of running a trained model to get predictions or responses.
Simple analogy: Using a trained chef (model) to cook meals (generate outputs) based on orders (prompts).
Why it matters: SLMs provide faster, cheaper inference than LLMs.
Why Small Language Models Matter
1. Democratizing AI Access
Not everyone can afford expensive GPU servers or cloud APIs. SLMs allow:
- Small businesses to deploy AI affordably
- Developers to run models on laptops
- Students to experiment without cloud costs
2. Privacy and Data Sovereignty
With SLMs, your data stays local:
- No sensitive data sent to external servers
- Compliance with PDPA, GDPR, and local regulations
- Full control over your AI interactions
3. Reduced Environmental Impact
SLMs require less energy:
- Lower carbon footprint per inference
- Sustainable AI deployment at scale
- Green computing initiatives
4. Real-World Deployment
Many real applications need SLMs:
- Mobile apps can't rely on constant connectivity
- Edge devices have limited computing power
- Production systems need predictable latency
How Small Language Models Work
The Training Process
- Start with an Architecture: Design a compact neural network
- Pre-training: Learn from large text datasets (general knowledge)
- Fine-tuning: Specialize for specific tasks or languages
- Optimization: Apply quantization, pruning, or distillation
- Deployment: Package for target platform (mobile, edge, server)
Running an SLM
When you send a prompt to an SLM:
- Tokenization: Text is converted to numbers
- Embedding: Numbers become vectors
- Processing: Vectors pass through neural network layers
- Generation: Model predicts the next token
- Output: Tokens are converted back to text
The key difference is that SLMs have fewer layers and smaller dimensions, making each step faster.
Small Language Models in Thailand
Chinda Thai LLM: Thailand's Open-Source SLM
Chinda is a 4-billion parameter model developed by iApp Technology specifically for Thai language:
Key Features:
- Thai-Optimized: Fine-tuned on Thai text for natural responses
- Compact: Only 4B parameters - runs on consumer hardware
- Open Source: Available on Hugging Face
- FREE API: No cost until December 31, 2025
Why Chinda is Perfect for Thai Applications:
- Understands Thai grammar and particles (ครับ/ค่ะ)
- Handles Thai-English code-switching
- Cultural context awareness
- Local deployment possible
Example: Running Chinda Locally
You can run Chinda on your own computer using tools like:
Example: Using Chinda API
import requests
response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/v3/llm/chinda-thaillm-4b/chat/completions',
headers={
'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
json={
'model': 'chinda-qwen3-4b',
'messages': [
{'role': 'user', 'content': 'อธิบายความแตกต่างระหว่าง SLM และ LLM'}
],
'max_tokens': 1024
}
)
print(response.json())
Real-World Applications in Thailand
1. Thai Customer Service Chatbots
Deploy Chinda on your servers to handle Thai customer queries:
- No per-request API costs
- Full data privacy
- Works offline or in air-gapped environments
2. Thai Document Processing
Combine SLMs with Thai OCR:
- Extract text from Thai documents
- Summarize or classify content locally
- Process sensitive documents without cloud exposure
3. Mobile Thai Voice Assistants
Pair with Speech-to-Text and Text-to-Speech:
- On-device voice interaction
- Real-time Thai speech recognition
- Natural Thai speech synthesis
4. Edge AI for Thai Retail
Deploy on local servers in stores:
- Product recommendation without internet
- Inventory management AI
- Customer analytics with privacy
Getting Started with Small Language Models
Option 1: Use iApp's Chinda API (Easiest)
- Create account: Visit iApp.co.th
- Get API key: Go to API Key Management
- Start building: Use the simple REST API
- Cost: FREE until December 31, 2025
Option 2: Run Locally (Most Private)
- Download model: Get Chinda from Hugging Face
- Install runtime: Use LM Studio or Ollama
- Run locally: No internet required
- Cost: Only your hardware
Option 3: Deploy On-Premise (Enterprise)
- Contact iApp: Contact us
- Custom setup: Tailored to your infrastructure
- Support: Enterprise SLA and training
- Cost: One-time license + support
Comparing iApp's AI Models
| Model | Type | Parameters | Best For | Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinda Thai LLM 4B | SLM | 4B | Thai chatbots, local deployment | FREE |
| DeepSeek-V3.2 | LLM | 685B | Complex reasoning, coding | 0.01 IC/1K tokens |
| Thanoy Legal AI | Domain SLM | - | Thai legal documents | Token-based |
The Future of Small Language Models
Trends to Watch
- On-Device AI: Every smartphone will have capable SLMs
- Specialized Models: Industry-specific SLMs (medical, legal, financial)
- Hybrid Systems: SLMs for simple queries, LLMs for complex ones
- Better Efficiency: Same capability with fewer parameters
- Thai Language Focus: More models optimized for Thai
Why This Matters for Thai Businesses
- Cost Savings: Reduce AI infrastructure costs by 90%+
- Data Sovereignty: Keep Thai data in Thailand
- Competitive Edge: Deploy AI faster than competitors
- Innovation: Build products impossible with cloud-only AI
Conclusion
Small Language Models represent a fundamental shift in AI deployment - from centralized cloud computing to distributed, efficient, privacy-preserving AI. They're not a replacement for LLMs but a complement, enabling AI in scenarios where large models simply can't go.
For Thai businesses and developers, SLMs like Chinda offer an unprecedented opportunity to build AI-powered applications that are fast, affordable, and respect user privacy.
Ready to get started? Sign up for free and try Chinda Thai LLM - Thailand's own Small Language Model!
Questions? Join our Discord Community or email us at support@iapp.co.th.
iApp Technology Co., Ltd. Thailand's Leading AI Technology Company