What is a Chatbot? A Complete Guide for Beginners
Have you ever chatted with customer support on a website at 2 AM and gotten an instant reply? Or asked a voice assistant to play music or check the weather? Chances are, you were talking to a chatbot. These AI-powered conversational agents are transforming how businesses interact with customers, and they're becoming smarter every day.
What is a Chatbot?
A chatbot is a computer program designed to simulate human conversation. It can communicate through text messages, voice, or both, and is used to automate interactions with users.
At its core, a chatbot:
- Receives user messages (text or voice)
- Understands what the user wants
- Generates appropriate responses
- Takes actions when needed (like booking appointments or processing orders)
Chatbots range from simple rule-based systems that follow scripts to sophisticated AI systems that understand context, remember previous conversations, and learn from interactions.
Simple Example
Basic Chatbot:
- User: "What are your business hours?"
- Bot: "Our business hours are Monday to Friday, 9 AM to 6 PM."
AI-Powered Chatbot:
- User: "I ordered something last week but it hasn't arrived yet"
- Bot: "I'm sorry to hear that. Let me look up your recent orders... I found order #12345 placed on December 2nd. It shows as 'In Transit' and should arrive by tomorrow. Would you like me to send you the tracking link?"
Types of Chatbots
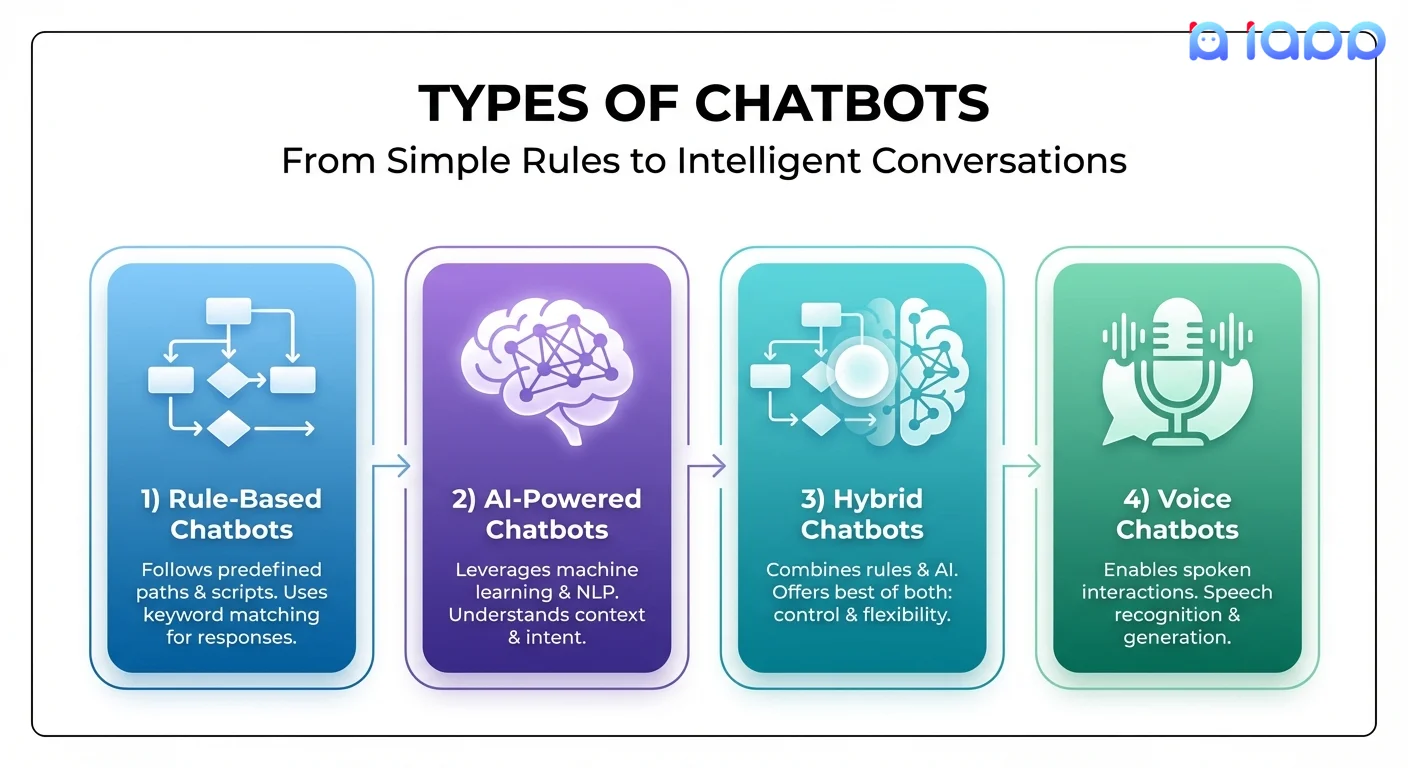
1. Rule-Based Chatbots
The simplest type that follows predefined rules and decision trees.
How they work:
- Match keywords in user messages
- Follow if-then logic
- Present menu options for users to choose
Pros: Simple to build, predictable responses, low cost Cons: Can't handle unexpected questions, limited flexibility
Best for: FAQs, simple menu navigation, basic information lookup
2. AI-Powered Chatbots (NLU-based)
Use Natural Language Understanding to interpret user intent.
How they work:
- Analyze the meaning behind messages
- Identify user intent and extract key information
- Generate contextual responses
Pros: Understand natural language, handle variations, more human-like Cons: Require training data, more complex to build
Best for: Customer service, lead qualification, support tickets
3. LLM-Powered Chatbots
The latest generation using Large Language Models like GPT or Thai LLMs.
How they work:
- Use massive AI models trained on billions of texts
- Generate human-like responses dynamically
- Can be customized with specific knowledge
Pros: Highly flexible, natural conversations, can handle complex queries Cons: Higher cost, potential for unexpected responses
Best for: Complex customer inquiries, content generation, personalized assistance
4. Voice Chatbots
Chatbots that communicate through speech instead of (or in addition to) text.
How they work:
- Convert speech to text (STT)
- Process the text with NLU/LLM
- Convert response back to speech (TTS)
Pros: Hands-free interaction, accessible, natural communication Cons: Require good speech recognition, accent/dialect challenges
Best for: Call centers, voice assistants, accessibility applications
5. Hybrid Chatbots
Combine rule-based logic with AI capabilities.
How they work:
- Use rules for common, predictable scenarios
- Fall back to AI for complex or unexpected queries
- Seamlessly hand off to human agents when needed
Pros: Best of both worlds, controlled yet flexible Cons: More complex architecture
Best for: Enterprise customer service, banking, healthcare
Key Chatbot Terms Explained (Jargon Buster)
1. Intent
What it is: The goal or purpose behind a user's message.
Simple analogy: Like understanding someone's "request" regardless of how they phrase it.
Example:
- "What's my balance?" → Intent:
check_balance - "How much money do I have?" → Intent:
check_balance - "Show me my account" → Intent:
check_balance
All three have the same intent, just phrased differently.
2. Entity
What it is: Specific pieces of information extracted from a message.
Simple analogy: The "details" that fill in the blanks of a request.
Example:
- "Book a flight to Bangkok on Friday"
- Intent:
book_flight - Entities: destination=
Bangkok, date=Friday
- Intent:
3. NLU (Natural Language Understanding)
What it is: The AI technology that interprets human language to extract meaning.
Simple analogy: Like a translator that converts human speech into structured data the computer can act on.
Components:
- Intent classification (what does the user want?)
- Entity extraction (what are the specific details?)
- Sentiment analysis (is the user happy or frustrated?)
4. Fallback
What it is: What the chatbot does when it doesn't understand the user.
Simple analogy: Like saying "I didn't catch that, could you rephrase?" instead of giving a wrong answer.
Good fallback strategies:
- Ask for clarification
- Offer alternative options
- Transfer to human agent
- Suggest related topics
5. Context / Conversation Memory
What it is: The chatbot's ability to remember previous messages in the conversation.
Simple analogy: Like how humans remember what was said earlier in a conversation.
Example:
- User: "I want to order pizza"
- Bot: "What size would you like?"
- User: "Large"
- Bot: "One large pizza. What toppings?" (remembers the pizza context)
Without context, the bot wouldn't know "large" refers to pizza size.
Why Chatbots Matter
1. 24/7 Availability
Chatbots never sleep, take breaks, or go on vacation. They can serve customers around the clock, even during holidays.
2. Instant Response
No waiting in queue. Customers get immediate answers to their questions, improving satisfaction.
3. Cost Efficiency
A single chatbot can handle thousands of conversations simultaneously, reducing the need for large customer service teams.
4. Consistency
Chatbots give the same accurate information every time, eliminating human errors and mood variations.
5. Scalability
During peak times (sales, promotions, crises), chatbots handle the surge without additional hiring.
6. Data Collection
Every conversation provides valuable data about customer needs, common issues, and improvement opportunities.
What Problems Do Chatbots Solve?
| Problem | Traditional Solution | Chatbot Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Long wait times | More staff | Instant responses 24/7 |
| Repetitive questions | FAQ pages (rarely read) | Interactive, personalized answers |
| After-hours support | Limited or none | Always available |
| Language barriers | Multilingual staff (expensive) | AI translation integration |
| High support costs | Large teams | Automated first-line support |
| Inconsistent answers | Training & QA | Standardized responses |
| Lead qualification | Manual screening | Automated qualification |
How Chatbots Work
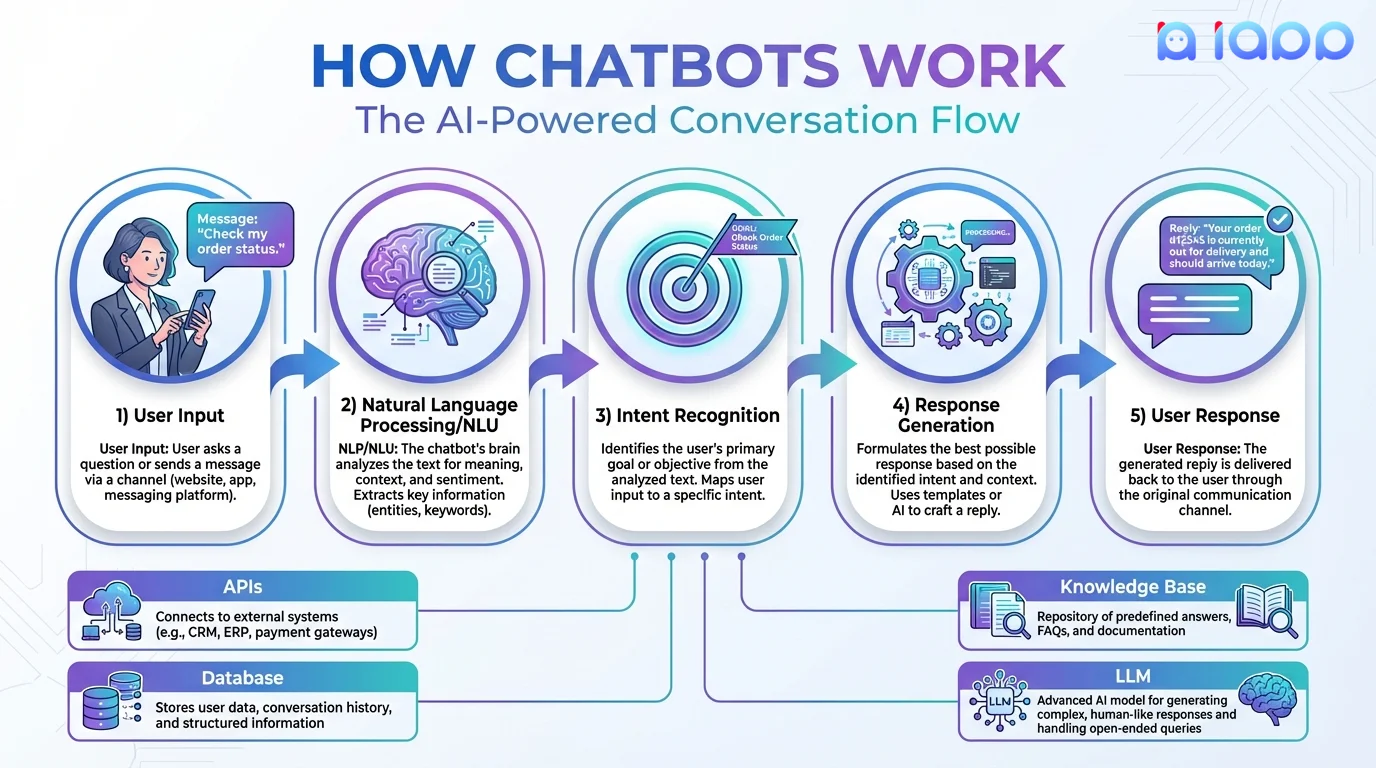
The Conversation Flow
-
User Input
- User types a message or speaks
- Input is captured by the chat interface
-
Natural Language Processing
- Text is analyzed for meaning
- Intent is identified
- Entities are extracted
- Context from previous messages is considered
-
Dialog Management
- Determines what action to take
- May query databases or APIs
- Decides on the response strategy
-
Response Generation
- Creates appropriate reply
- May use templates or AI generation
- Formats for the channel (text, voice, rich media)
-
Output Delivery
- Response sent back to user
- May include buttons, images, or audio
- Conversation state is saved
Architecture Example
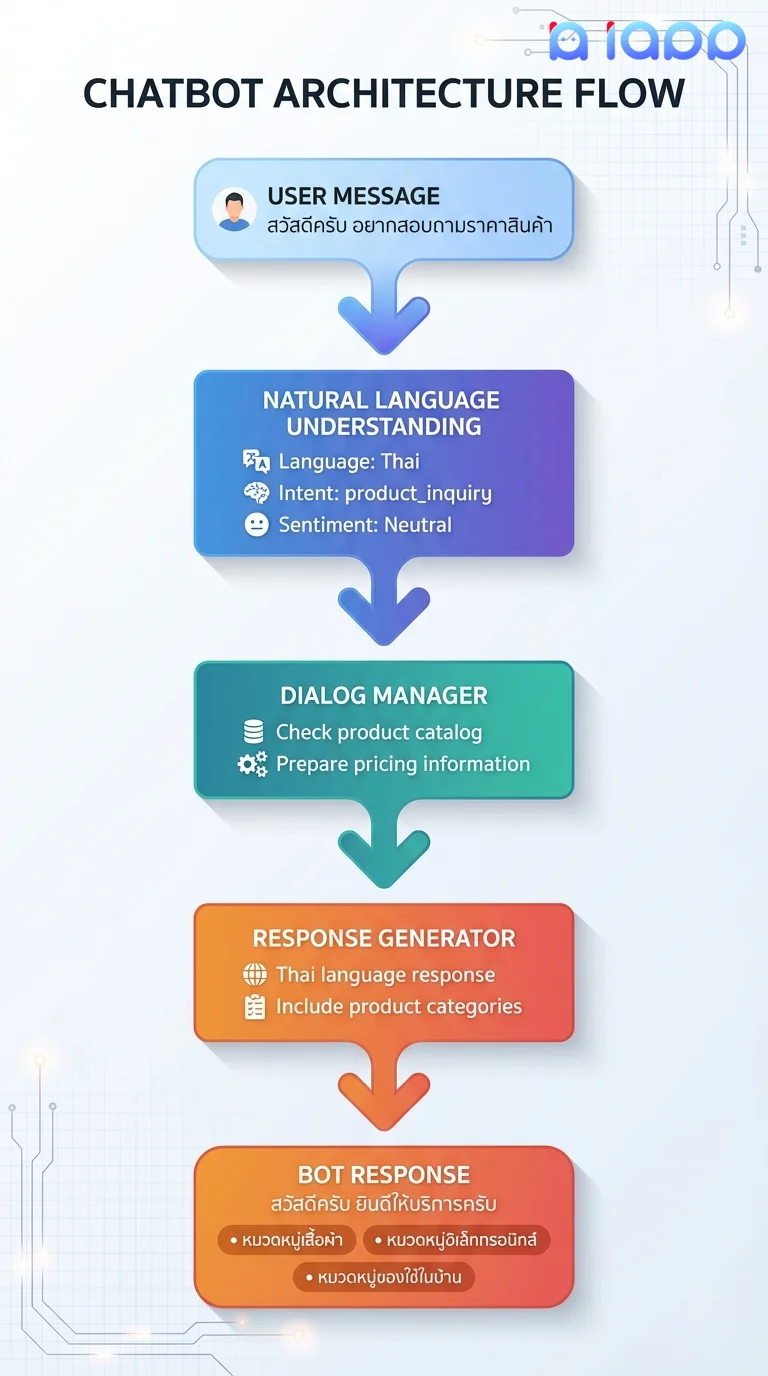
Chatbots in Thailand: Real Applications
1. Thai Language Customer Service
Using Chinda Thai LLM:
- Understands Thai language nuances and polite particles
- Handles Thai script and transliteration
- Responds naturally in Thai
- Understands context and cultural references
2. Voice-Enabled Thai Chatbots
Combining Speech-to-Text and Text-to-Speech:
- Accept voice input in Thai
- Process with Thai-optimized AI
- Respond with natural Thai speech
- Perfect for IVR and call centers
3. Multilingual Support
Using Translation API:
- Serve customers in Thai, English, Chinese, Japanese
- Auto-detect customer language
- Translate in real-time
- Maintain conversation context across languages
4. Document-Assisted Chatbots
Combining chatbots with Thai OCR:
- Upload ID cards or documents in chat
- Extract information automatically
- Process applications conversationally
- Streamline eKYC workflows
5. Legal and Specialized Knowledge
Using Thanoy Legal AI:
- Answer Thai legal questions
- Cite relevant laws and regulations
- Explain legal concepts simply
- Available 24/7 for preliminary guidance
Building Chatbots with iApp
iApp Technology provides the building blocks for Thai chatbots:
Available Components�
| Component | iApp Product | Role in Chatbot |
|---|---|---|
| Thai Language Brain | Chinda Thai LLM | Understanding and generating Thai |
| Advanced Reasoning | DeepSeek-V3.2 | Complex queries and analysis |
| Legal Knowledge | Thanoy Legal AI | Thai legal expertise |
| Voice Input | Speech-to-Text | Convert speech to text |
| Voice Output | Text-to-Speech | Natural Thai speech |
| Translation | Translation API | Multilingual support |
Example: Building a Thai Customer Service Chatbot
import requests
def thai_chatbot(user_message, conversation_history=[]):
"""
Simple Thai chatbot using Chinda LLM
"""
# Build conversation context
messages = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": """คุณเป็นผู้ช่วยบริการลูกค้าของบริษัท iApp Technology
ตอบคำถามด้วยความสุภาพและเป็นมิตร
ช่วยเหลือเรื่องผลิตภัณฑ์ AI และ API ต่างๆ
ถ้าไม่แน่ใจ ให้แนะนำติดต่อทีมสนับสนุน"""
}
]
# Add conversation history
messages.extend(conversation_history)
# Add current message
messages.append({
"role": "user",
"content": user_message
})
# Call Chinda Thai LLM
response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/v3/llm/chinda-thaillm-4b/chat/completions',
headers={
'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY',
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
json={
'model': 'chinda-qwen3-4b',
'messages': messages,
'max_tokens': 512,
'temperature': 0.7
}
)
result = response.json()
bot_reply = result['choices'][0]['message']['content']
# Update conversation history
conversation_history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_message})
conversation_history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": bot_reply})
return bot_reply, conversation_history
# Example usage
history = []
reply, history = thai_chatbot("สวัสดีครับ อยากสอบถามเรื่อง API", history)
print(reply)
reply, history = thai_chatbot("มี API อะไรบ้างครับ", history)
print(reply)
Example: Voice-Enabled Chatbot
import requests
def voice_chatbot(audio_file):
"""
Voice chatbot: Speech → Text → AI → Speech
"""
# Step 1: Convert speech to text
stt_response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/thai-speech-to-text/v2',
headers={'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY'},
files={'file': audio_file}
)
user_text = stt_response.json()['transcript']
# Step 2: Process with LLM
bot_reply, _ = thai_chatbot(user_text)
# Step 3: Convert text to speech
tts_response = requests.post(
'https://api.iapp.co.th/thai-text-to-speech/v1',
headers={'apikey': 'YOUR_API_KEY'},
json={
'text': bot_reply,
'voice': 'female',
'speed': 1.0
}
)
return {
'user_said': user_text,
'bot_reply': bot_reply,
'audio': tts_response.content
}
Getting Started with Chatbots
Step 1: Define Your Use Case
Common starting points:
- FAQ Bot: Answer common questions about your business
- Lead Bot: Qualify potential customers
- Support Bot: Handle basic support requests
- Booking Bot: Schedule appointments or reservations
Step 2: Choose Your Platform
Where will your chatbot live?
- Website widget
- LINE Official Account
- Facebook Messenger
- Mobile app
- Phone/IVR system
Step 3: Build with iApp APIs
- Get your API key
- Start with Chinda Thai LLM for Thai language
- Add Speech APIs for voice
- Integrate with your preferred platform
Resources
- Get API Access: API Key Management
- Try Chinda: Thai LLM Demo
- Try Speech APIs: Speech-to-Text Demo
- Explore All APIs: Complete API Catalog
- Join Community: Discord
The Future of Chatbots
Trends to Watch
- More Human-Like: LLMs making conversations indistinguishable from humans
- Multimodal: Chatbots that see images, hear voice, and read documents
- Proactive: Bots that initiate helpful conversations, not just respond
- Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and responding to user emotions
- Autonomous Actions: Bots that can complete complex tasks end-to-end
Why Thai Businesses Should Act Now
- Customer Expectations: Users expect instant, 24/7 responses
- Competitive Advantage: Stand out with superior customer experience
- Cost Savings: Reduce support costs while improving service
- Data Insights: Learn from thousands of customer conversations
- Scalability: Handle growth without proportional cost increases
Conclusion
Chatbots have evolved from simple rule-based responders to sophisticated AI assistants that can understand Thai language, process voice, and handle complex conversations. They're no longer a "nice to have" but essential for businesses that want to provide excellent customer service at scale.
With iApp Technology's suite of Thai-optimized AI APIs — Chinda Thai LLM for language understanding, Speech APIs for voice interaction, and Translation for multilingual support — Thai businesses can build world-class chatbots that truly understand their customers.
Ready to build your first Thai chatbot? Sign up for free and start with Chinda Thai LLM today!
Questions? Join our Discord Community or email us at support@iapp.co.th.
iApp Technology Co., Ltd. Thailand's Leading AI Technology Company